"VSports app下载" Effectiveness of a Flossing Protocol and Manual Therapy in Improving the Clinical and Functional Status of Subjects with Recurrent Ankle Sprains; A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 40843771
- PMCID: PMC12372161
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci13030149
Effectiveness of a Flossing Protocol and Manual Therapy in Improving the Clinical and Functional Status of Subjects with Recurrent Ankle Sprains; A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
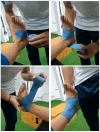
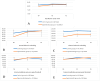
Introduction: Recurrent ankle sprains can lead to chronic ankle instability VSports手机版. The flossing technique aims to modify the function and characteristics of fascial tissue. The objective was to evaluate the effectiveness of flossing and sliding techniques in improving subjects with previous ankle sprains. Methods: Randomized, double-blind clinical study with a follow-up period. Twenty-six subjects were assigned to two study groups: experimental (flossing technique and passive manual therapy techniques) and placebo control group (flossing technique without compression and manual therapy techniques without sliding). The intervention lasted three weeks, with two sessions per week. The study variables were dorsiflexion under load (Leg Motion®), ankle mobility under unloaded conditions (goniometer), pressure pain threshold (algometer), and stability (Rs Scan® pressure platform). Three measurements were taken: pre-treatment (T0), post-treatment (T1), and after 3 weeks of follow-up (T2). Results: There were significant intergroup differences in dorsiflexion under load (F = 4. 90; p = 0. 02). Range of motion in plantar flexion without load (F = 3. 78; p = 0. 04), in the ellipse area (F = 4. 72; p = 0. 01), left stability (F = 3. 74; p = 0. 03), and right stability (F = 3. 73; p = 0. 03) without visual support. Conclusions: A physiotherapy protocol using flossing and manual sliding therapy can increase loaded dorsal flexion in young adults with previous ankle sprains. This intervention can also improve ankle plantar flexion under unloaded conditions. The area of the ellipse without visual support can improve in young adults with a history of ankle sprains following a program of flossing and manual therapy. .
Keywords: flossing; manual therapy; pressure pain threshold; range of motion; sprain; stability. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References (VSports最新版本)
-
- Gribble P.A., Bleakley C.M., Caulfield B.M., Docherty C.L., Fourchet F., Fong D.T., Hertel J., Hiller C.E., Kaminski T.W., O McKeon P., et al. Evidence review for the 2016 International Ankle Consortium consensus statement on the prevalence. impact and long-term consequences of lateral ankle sprains. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016;50:1496–1505. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-096189. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Golditz T., Welsch G.H., Pachowsky M., Hennig F.F., Pfeifer K., Steib S. A multimodal approach to ankle instability: Interrelations between subjective and objective assessments of ankle status in athletes. J. Orthop. Res. 2016;34:525–532. doi: 10.1002/jor.23039. - DOI (V体育官网入口) - PubMed
-
- Carto C., Lezak B., Varacallo M. Anatomy Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb. Distal Tibiofibular Joint (Tibiofibular Syndesmosis) StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2019. - PubMed
-
- Aslan A., Sofu H., Kirdemir V. Ankle ligament injury: Current concept. OA Orthop. 2014;2:5–10.
Publication types
"V体育安卓版" MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports app下载" Medical

