Recruitment, adherence, and retention of endometrial cancer survivors in a behavioural lifestyle programme: the Diet and Exercise in Uterine Cancer Survivors (DEUS) parallel randomised pilot trial
- PMID: 28993394
- PMCID: PMC5640120
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018015 (VSports app下载)
"VSports注册入口" Recruitment, adherence, and retention of endometrial cancer survivors in a behavioural lifestyle programme: the Diet and Exercise in Uterine Cancer Survivors (DEUS) parallel randomised pilot trial
Abstract
Objective: Healthy eating and physical activity may help endometrial cancer survivors (ECS) improve their quality of life. However, most ECS do not meet the relevant guidelines. This pilot trial aimed to test the study feasibility procedures for a definitive trial of a behavioural lifestyle programme. VSports手机版.
Design and setting: This 24-week parallel two-arm randomised pilot trial took place in two hospitals in London, UK (April 2015-June 2016). V体育安卓版.
Participants: Sixty disease-free ECS within 3 years of diagnosis. V体育ios版.
Interventions: Participants were randomised using minimisation to receive the intervention or care as usual. The 'Shape-Up following cancer treatment' programme used self-monitoring, goal-setting, self-incentives, problem-solving and group social support for 12 hours over 8 weeks to help survivors improve their eating and physical activity VSports最新版本. .
Outcome measures: The main outcome measures were recruitment, adherence, and retention rates. Further outcomes included barriers to participation and feedback on programme satisfaction. V体育平台登录.
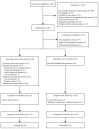
Results: Of the 296 potentially eligible ECS, 20% (n=60) were randomly allocated to the active intervention (n=29) or control group (n=31). Three participants in each arm were deemed ineligible after randomisation and excluded from analysis VSports注册入口. Twenty participants (77%; 95% CI 61% to 93%) adhered to the intervention and provided generally favourable feedback. At 24 weeks, 25/26 (96%; 95% CI 89% to 100%) intervention and 24/28 (86%; 95% CI 73% to 99%) control participants completed their assessment. No intervention-related adverse events were reported. Among eligible survivors who declined study participation (n=83), inconvenience (78%; 95% CI 69% to 87%) was the most common barrier. .
Conclusions: The trial was feasible to deliver based on the a priori feasibility criteria V体育官网入口. Enhancing recruitment and adherence in a definitive trial will require designs that promote convenience and consider ECS-reported barriers. .
Trial registration number: NCT02433080; Pre-results. VSports在线直播.
Trial funding: University College London, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Nurses League, and NIHR University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre.
Keywords: Endometrial cancer; behaviour change; healthy eating; intervention; physical activity; survivorship.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
V体育安卓版 - Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DAK and RJB are volunteers for the charity Weight Concern, which developed the original Shape-Up programme for the general population. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, et al. . Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 2017;3:524–48. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ward KK, Shah NR, Saenz CC, et al. . Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among endometrial cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol 2012;126:176–9. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.04.013 - DOI (VSports app下载) - PubMed
-
- Koutoukidis DA, Knobf MT, Lanceley A. Obesity, diet, physical activity, and health-related quality of life in endometrial cancer survivors. Nutr Rev 2015;73:399–408. 10.1093/nutrit/nuu063 - "V体育ios版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (VSports app下载)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Associated data
V体育ios版 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
V体育ios版 - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous