VSports手机版 - Building discontinuous liver sinusoidal vessels
- PMID: 28218626
- PMCID: PMC5330719
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI92823
Building discontinuous liver sinusoidal vessels
Abstract
Blood vessels have a unified mission to circulate blood throughout the body; however, they have additional diverse and specialized roles in various organs. For example, in the liver, discontinuous sinusoids, which are fenestrated capillaries with intercellular gaps and a fragmented basement membrane, facilitate delivery of macromolecules to highly metabolic hepatocytes. During embryonic development, discontinuous sinusoids also allow circulating hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells to populate the liver and promote blood cell differentiation. In this issue of the JCI, Géraud et al. describe an essential role for the transcription factor GATA4 in promoting the development of discontinuous sinusoids VSports手机版. In the absence of liver sinusoidal GATA4, mouse embryos developed hepatic capillaries with upregulated endothelial cell junction proteins and a continuous basement membrane. These features prevented hematopoietic progenitor cells from transmigrating into the developing liver, and Gata4-mutant embryos died from subsequent liver hypoplasia and anemia. This study highlights the surprising and extensive transcriptional control GATA4 exercises over specialized liver vascular development and function. .
V体育2025版 - Conflict of interest statement
Figures
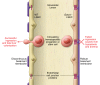
Comment on (VSports手机版)
- GATA4-dependent organ-specific endothelial differentiation controls liver development and embryonic hematopoiesis
References (V体育官网入口)
-
- Pavelka M, Roth J. Functional Ultrastructure: Atlas of Tissue Biology and Pathology. Vienna, Austria: Springer Vienna; 2010:254–255.
-
- Sarin H. Physiologic upper limits of pore size of different blood capillary types and another perspective on the dual pore theory of microvascular permeability. J Angiogenes Res. 2010;2:14. - V体育2025版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gomez Perdiguero E, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. 2015;518(7540):547–551. - "V体育官网入口" PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

