Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer
- PMID: 29702599
- PMCID: PMC5983611
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19051310
Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer (VSports最新版本)
Abstract
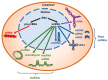
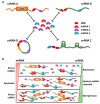
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) constitute the majority of the human transcribed genome. This largest class of RNA transcripts plays diverse roles in a multitude of cellular processes, and has been implicated in many pathological conditions, especially cancer. The different subclasses of ncRNAs include microRNAs, a class of short ncRNAs; and a variety of long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), such as lincRNAs, antisense RNAs, pseudogenes, and circular RNAs. Many studies have demonstrated the involvement of these ncRNAs in competitive regulatory interactions, known as competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks, whereby lncRNAs can act as microRNA decoys to modulate gene expression. These interactions are often interconnected, thus aberrant expression of any network component could derail the complex regulatory circuitry, culminating in cancer development and progression VSports手机版. Recent integrative analyses have provided evidence that new computational platforms and experimental approaches can be harnessed together to distinguish key ceRNA interactions in specific cancers, which could facilitate the identification of robust biomarkers and therapeutic targets, and hence, more effective cancer therapies and better patient outcome and survival. .
Keywords: cancer; ceRNA; circRNA; lncRNA; miRNA; pseudogene. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References (VSports最新版本)
-
- Carninci P., Kasukawa T., Katayama S., Gough J., Frith M.C., Maeda N., Oyama R., Ravasi T., Lenhard B., Wells C., et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–1563. - PubMed
-
- Cech T.R., Steitz J.A. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157:77–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.008. - VSports app下载 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports" Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports" Other Literature Sources

