V体育2025版 - Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by conventional, novel, and atypical protein kinase C isotypes
- PMID: 9447975
- PMCID: "V体育ios版" PMC108790
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.2.790
VSports app下载 - Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by conventional, novel, and atypical protein kinase C isotypes
V体育安卓版 - Abstract
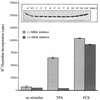
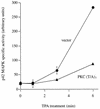
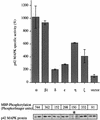
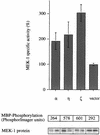
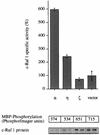
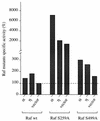
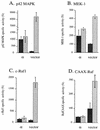
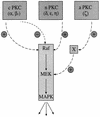
Phorbol ester treatment of quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells leads to cell proliferation, a response thought to be mediated by protein kinase C (PKC), the major cellular receptor for this class of agents. We demonstrate here that this proliferation is dependent on the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) cascade. It is shown that dominant-negative PKC-alpha inhibits stimulation of the ERK/MAPK pathway by phorbol esters in Cos-7 cells, demonstrating a role for PKC in this activation VSports手机版. To assess the potential specificity of PKC isotypes mediating this process, constitutively active mutants of six PKC isotypes (alpha, beta, delta, epsilon, eta, and zeta) were employed. Transient transfection of these PKC mutants into Cos-7 cells showed that members of all three groups of PKC (conventional, novel, and atypical) are able to activate p42 MAPK as well as its immediate upstream activator, the MAPK/ERK kinase MEK-1. At the level of Raf, the kinase that phosphorylates MEK-1, the activation cascade diverges; while conventional and novel PKCs (isotypes alpha and eta) are potent activators of c-Raf1, atypical PKC-zeta cannot increase c-Raf1 activity, stimulating MEK by an independent mechanism. Stimulation of c-Raf1 by PKC-alpha and PKC-eta was abrogated for RafCAAX, which is a membrane-localized, partially active form of c-Raf1. We further established that activation of Raf is independent of phosphorylation at serine residues 259 and 499. In addition to activation, we describe a novel Raf desensitization induced by PKC-alpha, which acts to prevent further Raf stimulation by growth factors. The results thus demonstrate a necessary role for PKC and p42 MAPK activation in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate induced mitogenesis and provide evidence for multiple PKC controls acting on this MAPK cascade. .
Figures

References
-
- Adams P D, Parker P J. TPA-induced activation of MAP kinase. FEBS Lett. 1991;290:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S, Kozma R, Monfries C, Hall C, Lim H H, Smith P, Lim L. Human brain n-chimaerin cDNA encodes a novel phorbol ester receptor. Biochem J. 1990;272:767–773. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley D T, Saltiel A R. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Saito Y, Campbell D G, Cohen P, Sithanandam G, Rapp U, Ashworth A, Marshall C J, Cowley S. Identification of the sites in MAP kinase kinase-1 phosphorylated by p74raf-1. EMBO J. 1994;13:1610–1619. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Avruch J, Zhang X F, Kyriakis J M. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:279–283. - V体育官网 - PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
