Identification of hub gene and immune infiltration in Lyme disease revealed by weighted gene co-expression network analysis and machine learning (V体育官网入口)
- PMID: 41013556
- PMCID: PMC12465215
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-03108-y
Identification of hub gene and immune infiltration in Lyme disease revealed by weighted gene co-expression network analysis and machine learning
"VSports在线直播" Abstract
Introduction: Lyme disease (LD), caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), is a multisystem disorder with early symptoms such as erythema migrans and late manifestations including arthritis and neuroborreliosis. The molecular mechanisms driving tissue damage and inflammatory dysregulation in LD remain incompletely characterized. Given the central role of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in orchestrating immune responses, we aimed to identify optimal feature genes (OFGs) within PBMCs associated with LD pathogenesis and delineate their immune infiltration patterns using integrated bioinformatics VSports手机版. .
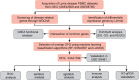
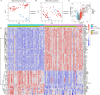
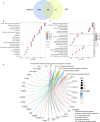
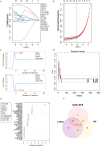
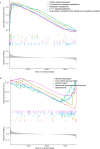
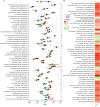
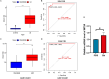
Methods: Transcriptomic datasets (GSE42606, GSE68765, GSE103481) were retrieved from GEO. Differential expression analysis identified LD-related genes. Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) screened disease-associated modules. Feature selection was performed via SVM-Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE), Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, and random forest (RF) to pinpoint OFGs. Immune cell infiltration was quantified using CIBERSORT, followed by correlation analysis between OFGs and immune subsets. The Single-gene gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed to explore the functional associations of OFGs. Biological pathways linked to OFGs were inferred by single-sample GSEA (ssGSEA). Diagnostic utility was assessed via ROC curves and nomogram modeling. Finally, we used RT-qPCR to confirm the bioinformatics results V体育安卓版. .
Results: Our study identified 174 DEGs among the LD patients, with 156 genes located within the "turquoise" module by WGCNA, exhibiting the most robust correlation with clinical characteristics. Among these, KIAA1199 turned out to be the unique OFG, selected via three distinct machine learning methodologies, possessing exceptional diagnostic potential. The Single-gene gene set enrichment analysis showed KIAA1199 was strongly correlated with multiple immune-related pathways V体育ios版. Furthermore, RT-qPCR validated candidate gene expression within a THP-1 cellular model. .
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study integrated WGCNA and machine learning methodologies to identify one core gene associated with LD from PBMC gene expression data: KIAA1199 VSports最新版本. The predictive model constructed using these genes demonstrated robust diagnostic accuracy, providing a basis for further research on host immune responses and the development of new diagnostic methods. .
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; Bioinformatics analysis; Immune infiltration; Machine learning (ML); Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) V体育平台登录. .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement (VSports在线直播)
Declarations VSports注册入口. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not required. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



VSports app下载 - References
-
- Mead P. Epidemiology of lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2022;36:495–521. 10.1016/j.idc.2022.03.004. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Kugeler KJ, Earley A, Mead PS, Hinckley AF. Surveillance for Lyme disease after implementation of a revised case definition - United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73:118–23. 10.15585/mmwr.mm7306a1. - "VSports最新版本" PMC - PubMed
-
- Wong KH, Shapiro ED, Soffer GK. A review of post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome and chronic Lyme disease for the practicing immunologist. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022;62:264–71. 10.1007/s12016-021-08906-w. - PubMed
-
- Miklossy J. Alzheimer’s disease - a neurospirochetosis. Analysis of the evidence following Koch’s and Hill’s criteria. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:90. 10.1186/1742-2094-8-90. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Medical
Research Materials

