Exploring the incidence potential of phenol-soluble modulins among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Lahore, Pakistan
- PMID: 41013425
- PMCID: PMC12465548
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-025-11350-2
Exploring the incidence potential of phenol-soluble modulins among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Lahore, Pakistan
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has emerged as a major clinical and epidemiological problem over the past few decades. This study aimed to investigate antibiotic resistance patterns, incidence potential of phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) genes and explored the associations between miscellaneous clinical specimens of MRSA and the incidence of virulent PSMs genes VSports手机版. .
Methods: This investigation employed a total of sixty MRSA strains isolated from clinical specimens such as pus aspirates, wound swabs, ear swabs, tissue swabs, blood, and urine. Antibiotic profiling was performed via Kirby-Bauer (KB) disk diffusion method. Genetic analysis was performed for detection of S. aureus-specific 16SrRNA gene, methicillin-resistant mecA and its homologue mecC gene and the virulent determinant PSMs genes psm-α, psm-β, and psm-mec along with agr operon gene via polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Pearson's Chi-square (χ2) analysis test was used to determine the associations between various clinical specimens and the incidence of PSMs genes, with a significance threshold set at p < 0 V体育安卓版. 05. .
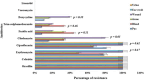
Results: Most of MRSA isolates were obtained from pus samples. The incidence of MRSA was more pronounced in males. Notably, the highest percentage of MRSA isolates was isolated from patients aged 21-40 years. Of all isolates (100%) harboured the 16SrRNA and mecA gene, whereas none of those isolates (0%) had the mecC gene. The resistance profiles of MRSA isolates obtained from various clinical specimens were not significantly different (p > 0. 05). Furthermore, vancomycin and linezolid were still effective for treating MRSA infections V体育ios版. Those 60 strains had 56/60 (93. 4%) psm-α, 54/60 (90%) psm-β, 55/60 (91. 6%) psm-mec and (48/60) 80% agr genes. A strong association was detected between the psm-β gene and MRSA strains obtained from pus samples (p = 0. 01), as was the case for the psm-mec gene and MRSA strains obtained from pus samples (p = 0. 03). .
Conclusion: The well-informed decisions could be made on the prescription of the best antibiotic therapy, the implementation of efficient control measures, and the development of anti-virulence strategies to stop the dissemination of MRSA in hospitals and clinical settings VSports最新版本. The virulence factors PSMs may be considered as potential candidates for treating virulent MRSA infections in patients through anti-virulence strategies. .
Keywords: MecA; MecC; Antibiotic resistance; MRSA; Phenol soluble modulins (PSMs) genes; Virulence determinant V体育平台登录. .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Institutional Research Ethics and Biosafety Committee (IREBC) of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan (Letter no. 197/20-2-23). This study followed the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional research ethics and biosafety committee. All enrolled participants provided written informed consent before sample collection for this institutionally approved cross-sectional study. All the data analysed during this study were kept confidential and anonymous. Consent for publication: This section was not applicable VSports注册入口. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Panwala T, Gandhi P, Jethwa D. Inducible clindamycin resistance and MRSA amongst Staphylococcus aureus isolates: a phenotypic detection. IP Int J Med Microbiol Trop Dis. 2020;6(4):222–6.
-
- Rajput A, Poudel S, Tsunemoto H, Meehan M, Szubin R, Olson CA, et al. Identifying the effect of Vancomycin on health care–associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains using bacteriological and physiological media. Gigascience. 2021;10(1): giaa156. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the united States. JAMA. 2007;298(15):1763–71. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources (V体育ios版)
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources
Medical
VSports - Miscellaneous

