"VSports" Design and Application of a Radiofrequency Spectrophotometry Sensor for Measuring Esophageal Liquid Flow to Detect Gastroesophageal Reflux
- PMID: 40969042
- PMCID: "VSports在线直播" PMC12158313
- DOI: 10.3390/s25113533
Design and Application of a Radiofrequency Spectrophotometry Sensor for Measuring Esophageal Liquid Flow to Detect Gastroesophageal Reflux (VSports在线直播)
"V体育官网入口" Abstract
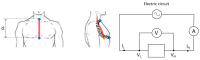
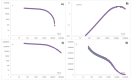
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a widespread condition that requires reliable and non-invasive diagnostic methods to minimize patient discomfort. This study presents a radiofrequency spectrophotometry sensor specifically designed to detect esophageal liquid flow and ionicity in real time without disrupting the patient's daily life. The sensor operates by measuring dielectric properties and ionic conductivity through the thoracic plexus, eliminating the need for invasive probes or prolonged monitoring. A study conducted on 49 participants demonstrated the sensor's ability to differentiate between various liquid media and identify beta dispersion relaxation as a biomarker for esophageal tissue damage, a key indicator of GERD progression. Additionally, alpha dispersion conductivity effectively distinguished reflux episodes, proving the sensor's high sensitivity VSports手机版. Unlike traditional diagnostic techniques such as endoscopy or pH monitoring, this radiofrequency spectrophotometry sensor enables continuous, real-time reflux detection, allowing patients to maintain a normal lifestyle during assessment. The results validate its potential as an innovative alternative for GERD diagnosis and monitoring, with future research focused on clinical validation, optimization, and integration into long-term patient monitoring systems. .
Keywords: GERD; bioimpedance; radiofrequency spectroscopy; reflux V体育安卓版. .
"VSports" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest V体育ios版. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures (VSports注册入口)





References
-
- Vakil N., van Zanten S.V., Kahrilas P., Dent J., Jones R., Global Consensus G. The Montreal Definition and Classification of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Global Evidence-Based Consensus. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. | ACG. 2006;101:1900–1920. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeong I.D. A Review of Diagnosis of GERD. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2017;69:96–101. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.2.96. - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin Y.L., Yao T., Wang Y.W., Zhou Z.X., Hong Z.C., Shen Y., Yan Y., Li Y.C., Lin J.F. Potential drug targets for gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s esophagus identified through Mendelian randomization analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2024;69:245–253. doi: 10.1038/s10038-024-01234-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schweckendiek D., Pohl D. Established and Novel Methods to Assess GERD: An Update. Visc. Med. 2024;40:331–338. doi: 10.1159/000540186. - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Grants and funding (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports最新版本 - Medical

