Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of HIIT in Individuals with Long COVID: Insights into the Potential Role of Triphala
- PMID: 40943540
- PMCID: PMC12428976
- DOI: "VSports app下载" 10.3390/ijms26178623
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of HIIT in Individuals with Long COVID: Insights into the Potential Role of VSports手机版 - Triphala
Abstract
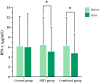
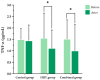
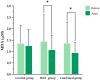
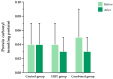
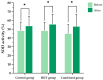
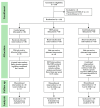
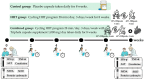
Long COVID is characterized by persistent symptoms associated with chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. While high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and supplementation with antioxidants such as Triphala have demonstrated individual therapeutic benefits, their combined effects remain unclear. This study aimed primarily to evaluate the effects of an 8-week HIIT program on markers of inflammation, oxidative stress, and exercise-related symptoms in individuals with long COVID, and secondarily to explore whether Triphala supplementation provided additional benefits. A total of 104 participants (aged 18-59 years) were randomized into three groups-control (placebo), HIIT (cycling for 28 min/day, 3 days/week), and combined (HIIT + Triphala, 1000 mg/day)-for 8 weeks. The biomarkers assessed included interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonyls, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Following the intervention, significant reductions in IFN-γ, TNF-α, MDA, protein carbonyls, and rating of perceived exertion were observed in both the HIIT and combined groups (p < 0. 05), with no significant differences between the two. SOD activity significantly increased in all groups, including the control group (p < 0. 05), with no between-group differences. An 8-week HIIT program appears to be effective in reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and dyspnea in individuals with long COVID VSports手机版. Triphala supplementation did not provide any additional statistically significant benefit but was safe and well tolerated. .
Keywords: exercise therapy; inflammation; long COVID; oxidative stress; phytotherapy. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 1 July 2025)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c.
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
VSports最新版本 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网 - Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Medical

