"V体育官网入口" The Feasibility and Acceptability of an App-Based Intervention Aimed at Improving Maternal Health Literacy Regarding Infant Play and Development: Mixed Methods Study
- PMID: 40906520
- PMCID: PMC12447011
- DOI: 10.2196/76517
"V体育平台登录" The Feasibility and Acceptability of an App-Based Intervention Aimed at Improving Maternal Health Literacy Regarding Infant Play and Development: Mixed Methods Study
Abstract
Background: Allowing infants access to unstructured, unrestricted play in their home environment is imperative for increasing healthy movement behaviors and, therefore, developmental outcomes VSports手机版. Interventions should equip mothers to provide opportunities for infant play as early as possible. Evaluating such interventions is necessary to understand the feasibility for scale-up and implementation in specific contexts. Furthermore, the appropriateness and relevance of standardized outcome measures in different ethnic and socioeconomic contexts should be determined to ensure validity. .
Objective: This study aimed to (1) test the feasibility and acceptability of an intervention aimed at improving maternal health literacy regarding infant play and development and (2) determine participants' understanding of the study outcome questionnaires. V体育安卓版.
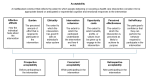
Methods: This mixed methods study was nested within the Play Love and You (PLAY) study, a randomized controlled trial (PACTR202202747620052) designed to promote infant development. Mothers assigned to the PLAY study intervention arm at 6 months post partum (n=68) received telephone or in-person check-ins and assessments every 2 months and health literacy intervention content and resources (videos and infographics) delivered via a mobile app every week V体育ios版. Feasibility was assessed by monitoring appointment attendance (adherence) and frequency of access to the content via the app. Acceptability was explored using a questionnaire and 2 participant focus group discussions (FGDs) at the end of the study (12 months post partum). The FGDs also included questions exploring the participants' understanding of the 4 study outcome measure questionnaires administered at both 6 and 12 months. .
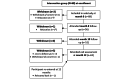
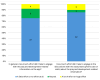
Results: In total, 68 participants were enrolled in the study at 6 months, of whom 17 (25%) attended the FGDs (n=8, 47% in FGD 1 and n=9, 53% in FGD 2). A total of 79% (49/62) of the participants completed the acceptability questionnaire VSports最新版本. The health literacy content was found to be highly acceptable based on qualitative and quantitative data. Most acceptability questions had 98% (48/49) positive answers. Participants enjoyed learning about active infant play and developmental milestones and how to make recycled toys. Over 80% of participants (62/68, 91%) attended the 12-month exit appointment. Most of the participants (47/62, 76%) could access the intervention content over the 12 months of the PLAY study, and of those, 60% (28/47) looked at content more than once a week, and 11% (5/47) did so every day. Less than a quarter (10/47, 21%) only looked at the content sporadically. Access was impacted by technical difficulties attributed to using inconsistent external service providers. .
Conclusions: This study was found to be acceptable to participants and feasible in this setting. The high acceptability of the intervention content and belief that other mothers would benefit from it suggests potential for effectiveness in similar communities V体育平台登录. However, the feasibility of app-based interventions relies on consistent and low-cost management of digital tools in low-resource settings. .
Keywords: acceptability; feasibility; infants; mHealth; maternal health literacy; mobile health; mothers; play and development. VSports注册入口.
©Fiona Bennin, Shane A Norris, Alessandra Prioreschi. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative. jmir. org), 04. 09. 2025. V体育官网入口.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
VSports手机版 - Figures


References
-
- Indrio F, Dargenio VN, Marchese F, Giardino I, Vural M, Carrasco-Sanz A, Pietrobelli A, Pettoello-Mantovani M. The importance of strengthening mother and child health services during the first 1000 days of life: the foundation of optimum health, growth and development. J Pediatr. 2022 Jun;245:254–6.e0. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.001.S0022-3476(22)00176-7 - DOI (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
-
- Carson V, Lee EY, Hewitt L, Jennings C, Hunter S, Kuzik N, Stearns JA, Unrau SP, Poitras VJ, Gray C, Adamo KB, Janssen I, Okely AD, Spence JC, Timmons BW, Sampson M, Tremblay MS. Systematic review of the relationships between physical activity and health indicators in the early years (0-4 years) BMC Public Health. 2017 Nov 20;17(Suppl 5):854. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4860-0. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-017-48... (VSports) 10.1186/s12889-017-4860-0 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eichner-Seitz N, Pate RR, Paul IM. Physical activity in infancy and early childhood: a narrative review of interventions for prevention of obesity and associated health outcomes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023;14:1155925. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1155925. "V体育官网" https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/37293499 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee RL, Lane S, Brown G, Leung C, Kwok SW, Chan SW. Systematic review of the impact of unstructured play interventions to improve young children's physical, social, and emotional wellbeing. Nurs Health Sci. 2020 Jun;22(2):184–96. doi: 10.1111/nhs.12732. - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kracht CL, Redman LM, Casey PH, Krukowski RA, Andres A. Association between home environment in infancy and child movement behaviors. Child Obes. 2021 Mar;17(2):100–9. doi: 10.1089/chi.2020.0319. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33471594 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding (V体育平台登录)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports" Full Text Sources
Medical

