Improving conscientiousness through a smartphone app and telecoaching intervention: insights from multiple sclerosis and healthy aging samples (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 40817184
- PMCID: "V体育ios版" PMC12356716
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-025-13320-9
V体育安卓版 - Improving conscientiousness through a smartphone app and telecoaching intervention: insights from multiple sclerosis and healthy aging samples
V体育ios版 - Abstract
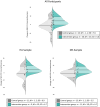
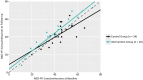
Lower Conscientiousness is associated with cognitive decline, unemployment, and poorer health outcomes in both neurological and aging populations. This study evaluated a smartphone-based intervention to enhance Conscientiousness in people with multiple sclerosis (PwMS) and healthy aging (HA) adults. Initially, 38 PwMS and 22 HA participants completed baseline assessments (cognitive, personality, depression, and anxiety measures). Attrition and disease factors left 24 PwMS and 20 HA adults at the 12-week follow-up. Participants randomly assigned to the intervention arm received the "Conscientiousness Coach" app, which combined value identification, SMART goal development, smartphone-based tracking, and scheduled telehealth coaching sessions, whereas controls were wait-listed. ANCOVA for baseline scores showed a significant treatment effect on NEO-FFI Conscientiousness (p = 0. 015) that remained after substituting age for diagnosis (p = 0. 029). A lack of significant effects for group (PwMS vs. HA) and age indicated that treatment impact was consistent across both samples. Within the intervention group, paired-sample t-tests revealed large gains in the Conscientiousness domain (d = 0. 93, p < 0. 001) and moderate improvements in the Orderliness (d = 0. 67, p = 0. 007) and Dependability (d = 0. 52, p = 0. 030) facets, with no change in wait-list controls VSports手机版. No treatment effects emerged for Neuroticism, depression, or anxiety, underscoring the trait-specific nature of the intervention. Results suggest that targeted digital interventions can favorably impact personality and enhance quality of life. Future study will examine use of AI to replace the behavioral coaching component of this intervention and its long-term impact on personality. .
Keywords: Conscientiousness; Functional impairment; Health aging; Multiple sclerosis; Personality intervention; Telecoaching V体育安卓版. .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interest: The authors declare the following competing interests: Author RHBB received honoraria, speaking, or consulting fees from Biogen, BMS, Celgene, EMD Serono, Merck, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi and has received research support from Biogen, BMS, Genzyme, NIH, NMSS, and Novartis. He has also received royalties from Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc. Author BWG served as a consultant for Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, Genentech, Celgene/Bristol Meyers Squibb, Sanofi Genzyme, Bayer, Janssen, Labcorp, and Horizon. She served in the speaker bureau for Biogen. She has also received grant/research support from the agencies listed in the previous sentence. She serves on the editorial board for BMJ Neurology, Children, CNS Drugs, MS International, and Frontiers Epidemiology. All other authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interests. Data availability: The dataset generated and analyzed during the current study is not publicly available but may be made available upon reasonable request and approval by the University at Buffalo institutional review board. The underlying code for this study is not publicly available for proprietary reasons V体育ios版.
Figures

V体育安卓版 - References
-
- Goldberg LR (1993) The structure of phenotypic personality traits,”. Am Psychol 48:26–34 - PubMed
-
- Digman JM (1990) Personality structure: emergence of the five-factor model,”. Anual Rev Psychol 41:417–440
-
- McCrae RR, Costa PT (1987) Validation of the five-factor model of personality across instruments and observers. J Pers Soc Psychol 52(1):81 - V体育官网 - PubMed
-
- Mukadam N et al (2024) Changes in prevalence and incidence of dementia and risk factors for dementia: an analysis from cohort studies. Lancet Public Health 9(7):e443–e460. 10.1016/S2468-2667(24)00120-8 - PubMed
-
- Maggio MG et al (2020) How personality traits affect functional outcomes in patients with multiple sclerosis: a scoping review on a poorly understood topic. Mult Scler Relat Disord 46:102560. 10.1016/j.msard.2020.102560 - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
"V体育官网" MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

