Serum Hemoglobin Level, Anemia, and Growth Were Unaffected by a 12-Month Multiple-Micronutrient Powder Intervention Among Children Aged 8-10 Months in a Low-Socioeconomic-Status Community of Jakarta
- PMID: 40806102
- PMCID: PMC12348989 (VSports手机版)
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17152520
Serum Hemoglobin Level, Anemia, and Growth Were Unaffected by a 12-Month Multiple-Micronutrient Powder Intervention Among Children Aged 8-10 Months in a Low-Socioeconomic-Status Community of Jakarta
Abstract
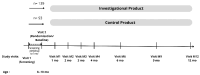
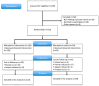
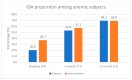
Background and Objectives: Anemia and stunting are major public health concerns for young Indonesian children. Limited information is available from studies on multi-micronutrient supplements in Indonesia. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of 12-month multi-micronutrient powder (MNP) supplementation on serum hemoglobin levels, anemia, and growth. Methods: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled study was performed, including 232 eligible children aged 8-10 months old. Children with severe anemia or stunting/those classed as underweight were not included as subjects VSports手机版. The study was performed in a low-socioeconomic-status community in Jakarta. With an active-to-placebo ratio of 60:40, 139 subjects received MNP sachets twice/day, and 93 subjects received placebo sachets, mixed with complementary food. The outcome parameters were hemoglobin level, anemia, and growth indicators. Per-protocol analysis was performed for 179 (intervention: 110; control: 69) subjects. Results: There were no differences at baseline between the groups, except for the weight-for-length z-scores (WLZ). Upon intervention, the serum hemoglobin level and anemia proportion did not change significantly within the group, and no significant differences were found between the groups (p > 0. 05). However, subgroup analysis of non-anemic children at baseline showed a significant increase in hemoglobin levels in the youngest age group (8. 0-8. 9 months old) receiving MNP compared to placebo (0. 13 vs. -0. 79, p = 0. 031). Iron deficiency anemia proportion showed a similar upward trend upon intervention in both groups. No significant differences in growth were found between both groups. Conclusions: This study failed to find a significant effect of 12-month MNP supplementation on serum hemoglobin level, anemia, and growth. .
Keywords: anemia; growth; hemoglobin level; infants 8–10 months; multi-micronutrient powder. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Guideline: Use of Multiple Micronutrient Powders for Point-of-Use Fortification of Foods Consumed by Infants and Young Children Aged 6–23 Months and Children Aged 2–12 Years. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Barkley J.S., Kendrick K.L., Codling K., Muslimatun S., Pachón H. Anemia prevalence over time in Indonesia: Estimates from the 1997, 2000, and 2008 Indonesia Family Life Surveys. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015;24:452–455. - PubMed
-
- Kusumadewi D., Bardosono S., Sekartini R. Dietary iron intake, serum ferritin and haemoglobin levels, and cognitive development scores of infants aged 6–8 months. Med. J. Indones. 2011;20:46–49. doi: 10.13181/mji.v20i1.427. - DOI
-
- De-Regil L.M., Suchdev P.S., Vist G.E., Walleser S., Peña-Rosas J.P. Home fortification of foods with multiple micronutrient powders for health and nutrition in children under 2 years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013;8:112–201. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1895. - "V体育2025版" DOI - PubMed
-
- Tam E., Keats E.C., Rind F., Das J.K., Bhutta A.Z.A. Micronutrient Supplementation and Fortification Interventions on Health and Development Outcomes among Children Under-Five in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:289. doi: 10.3390/nu12020289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

