Decoding the Tumor Microenvironment: Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and Therapeutic Frontiers
- PMID: 40612677
- PMCID: PMC12223767
- DOI: "VSports在线直播" 10.7150/ijbs.114222
VSports - Decoding the Tumor Microenvironment: Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and Therapeutic Frontiers
Abstract (VSports)
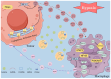
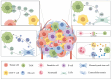
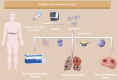
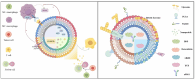
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is dynamically shaped by interactions between tumor cells, immune cells, and stromal components. Among these, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play dual roles in tumor progression. Exosomes are key mediators of intercellular communication and are crucial for modulating macrophage polarization. This review systematically summarizes the role of HIF-1α as the central regulator of tumor-derived exosomes under hypoxic conditions. Under endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways activation is mediated by the inactivation of the Hsp90/Hippo pathway, which induces the expression of LncRNA HMMR-AS1 and specific miRNAs (e. g. , miR-1246, let-7a, miR-301a-3p, etc. ). Furthermore, the IRE1/PERK pathway regulates exosome secretion by carrying miR-23a-3p and miR-27a-3p or directly delivering PD-L1 protein, thus activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, inhibiting PTEN, and upregulating PD-L1 expression as well as increasing the M2 polarization of macrophages. This study also summarized the important matrices of exosomes' involvement in the interaction between tumor cells and macrophages in different systemic malignant tumors. Moreover, the bidirectional crosstalk between TAM-derived exosomes and other TME components (e. g. , CD8+ T cells, fibroblasts) was also evaluated, which indicated their roles in immune evasion and metastasis VSports手机版. Further, engineering strategies, such as receptor-targeted exosomes and short palindromic repeats interference (CRISPRi)-based transcriptional silencing, were also discussed as emerging tools to enhance exosome specificity and therapeutic efficacy. This study proposes a roadmap for translating engineered exosomes into clinical immunotherapy regimens by integrating recent advances in spatial omics and artificial intelligence, and also addresses challenges in exosome isolation, stability, and biosafety. .
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures (V体育平台登录)

References
-
- Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2012;122:787–95. - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
-
- Locati M, Curtale G, Mantovani A. Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity. Annual review of pathology. 2020;15:123–47. - PMC (V体育平台登录) - PubMed
-
- Murray PJ. Macrophage Polarization. Annual review of physiology. 2017;79:541–66. - PubMed
"V体育官网入口" Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Substances
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

