Evaluation of the Efficacy and Accuracy of Super-Flexible Three-Dimensional Heart Models of Congenital Heart Disease Made via Stereolithography Printing and Vacuum Casting: A Multicenter Clinical Trial
- PMID: 39728278
- PMCID: PMC11677195
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd11120387 (VSports最新版本)
Evaluation of the Efficacy and Accuracy of Super-Flexible Three-Dimensional Heart Models of Congenital Heart Disease Made via Stereolithography Printing and Vacuum Casting: A Multicenter Clinical Trial
Abstract
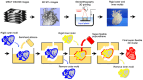
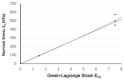
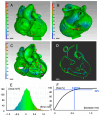
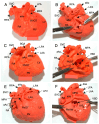
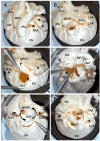
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is an advanced technology for accurately understanding anatomy and supporting the successful surgical management of complex congenital heart disease (CHD). We aimed to evaluate whether our super-flexible 3D heart models could facilitate preoperative decision-making and surgical simulation for complex CHD. The super-flexible heart models were fabricated by stereolithography 3D printing of the internal and external contours of the heart from cardiac computed tomography (CT) data, followed by vacuum casting with a polyurethane material similar in elasticity to a child's heart. Nineteen pediatric patients with complex CHD were enrolled (median age, 10 months). The primary endpoint was defined as the percentage of patients rated as "essential" on the surgeons' postoperative 5-point Likert scale. The accuracy of the models was validated by a non-destructive method using industrial CT. The super-flexible heart models allowed detailed anatomical diagnosis and simulated surgery with incisions and sutures. Thirteen patients (68 VSports手机版. 4%) were classified as "essential" by the primary surgeons after surgery, with a 95% confidence interval of 43. 4-87. 4%, meeting the primary endpoint. The product error within 90% of the total external and internal surfaces was 0. 54 ± 0. 21 mm. The super-flexible 3D heart models are accurate, reliable, and useful tools to assist surgeons in decision-making and allow for preoperative simulation in CHD. .
Keywords: 3D printing; clinical trial; congenital heart disease; heart surgery; simulation; stereolithography; vacuum casting V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
I. S. and K. K. received joint research funds from crossMedical Co. , Ltd V体育ios版. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

VSports在线直播 - References
-
- Erikssen G., Liestøl K., Seem E., Birkeland S., Saatvedt K.J., Hoel T.N., Døhlen G., Skulstad H., Svennevig J.L., Thaulow E., et al. Achievements in Congenital Heart Defect Surgery. A Prospective, 40-Year Study of 7038 Patients. Circulation. 2015;131:337–346, discussion 346. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.012033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stephens E.H., Graham G., Dearani J.A., Niaz T., Cetta F. Fontan Palliation in Patients with Heterotaxy Syndrome: A Five Decade Experience. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2022;13:436–442. doi: 10.1177/21501351221099944. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Erikssen G., Liestøl K., Aboulhosn J., Wik G., Holmstrøm H., Døhlen G., Gjesdal O., Birkeland S., Hoel T.N., Saatvedt K.J., et al. Preoperative versus postoperative survival in patients with univentricular heart: A nationwide, retrospective study of patients born in 1990–2015. BMJ Open. 2023;13:e069531. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069531. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources (VSports注册入口)
Full Text Sources

