Varying Course of External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve (EBSLN) and Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN) in Thyroidectomy-An Observational Study
- PMID: 38566684
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC10982202
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04465-y (VSports在线直播)
Varying Course of External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve (EBSLN) and Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN) in Thyroidectomy-An Observational Study (V体育平台登录)
Abstract
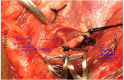
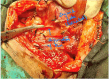
Surgical management of a diseased thyroid depends on sonological and pathological evaluation and thereby, planning of the surgery. The definite surgery has two objectives: removal of the diseased gland and preservation of the nerves, namely EBSLN (External Branch of Superior Laryngeal Nerve) and RLN (Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve) and the Parathyroid glands. The objectives of the study were: (1) To identify the course of the RLN and EBSLN of both sides, during Thyroidectomy VSports手机版. (2) To discern various anatomical landmarks, the relations of the two nerves with them and anatomical variations, if any. In this Prospective observational study, fifty selected goitre patients underwent various types of thyroidectomies based on sonological and cytological criteria. The course and anatomical variations of EBSLN and RLN were photo-documented and results were analysed. Most of the EBSLN were found as Cernea type 1 type (25 out of 50), followed by Cernea type 2a (comprising 36%). The least common was type 2b. It was found that 36 out of 50 (72%) of RLN passed posterior to Inferior Thyroid Artery (ITA). Moreover, before piercing cricothyroid joint, the RLN showed bifurcation in 13 out of 50 subjects (26%), 1 participant had trifurcation and the remaining 36 (72%) had a single trunk. The EBSLN shows relation to the horizontal plane passing through the upper pole of the thyroid gland and it is more prone to get damaged when it passes within less than 1 cm to the plane. The RLN has various relations to the distinct anatomical landmarks thereby helping in safe dissection of the nerve. The study also noted the RLN in relation to ITA and branching before entering into the cricothyroid joint. .
Keywords: Anatomical landmarks; Cricothyroid joint; Recurrent laryngeal nerve; Supeior laryngeal nerve; Thyroidectomy V体育安卓版. .
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023 V体育ios版. Springer Nature or its licensor (e. g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. .
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestAll the authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cernea CR, Ferraz AR, Nishio S, Dutra A Jr, Hojaij FC, dos Santos LR (1992) Sep-Oct;14(5):380-3 Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Head Neck. 10.1002/hed.2880140507. PMID: 1399571 - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
-
- Swapnali S, Bhuiyan PS. Relationship between the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the inferior thyroid artery: a study in cadavers. Int J Curr Res. 2016;9(09):38855–38557.
-
- Amana B, Foma W, Pegbessou E, Darré T, Boko E, Kpemissi E (2019) Apr Relationship between the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the inferior thyroid artery in the Togolese subject: Surgical anatomy study from 227 thyroidectomies. BJOHNS. 30 ;27(1)
-
- Zada B, Anwar K, Malik SA, Niamatullah, Khan N, Salam F (2014 Jul-Sep) Anatomical relationship between recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior thyroid artery in thyroidectomy patients. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 26(3):380–383 - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
VSports - Full Text Sources