Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer
- PMID: 36077769
- PMCID: PMC9454979
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14174232
Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer
VSports在线直播 - Abstract
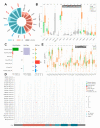
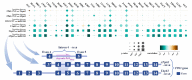
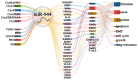
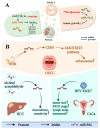
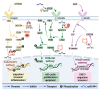
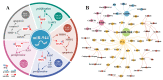
miRNA is a class of endogenous short-chain non-coding RNAs consisting of about 22 nucleotides. miR-944 is located in the fourth intron of the TP63 gene in the 3q28 region. miR-944 is abnormally expressed in cancers in multiple systems including neural, endocrine, respiratory, reproductive, and digestive systems. miR-944 can target at least 27 protein-coding genes. miR-944 can regulate a series of cell behaviors, such as cell cycle, proliferation, invasion and migration, EMT, apoptosis, etc. miR-944 participates in the networks of 11 ceRNAs, including six circRNAs and five lncRNAs. miR-944 is involved in three signaling pathways. The abnormal expression of miR-944 is closely related to the clinicopathological conditions of various cancer patients. Deregulated expression of miR-944 is significantly associated with clinicopathology and prognosis in cancer patients. In addition, miR-944 is also associated with the development of DDP, RAPA, DOX, and PTX resistance in cancer cells. miR-944 is involved in the anticancer molecular mechanisms of matrine and Rhenium-liposome drugs. In conclusion, this work systematically summarizes the related findings of miR-944, which will provide potential hints for follow-up research on miR-944 VSports手机版. .
Keywords: ceRNA; diagnosis; drug; dysregulation; miR-944; prognosis V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pereira T., Brito J.A.R., Guimaraes A.L.S., Gomes C.C., de Lacerda J.C.T., de Castro W.H., Coimbra R.S., Diniz M.G., Gomez R.S. MicroRNA profiling reveals dysregulated microRNAs and their target gene regulatory networks in cemento-ossifying fibroma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018;47:78–85. doi: 10.1111/jop.12650. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park S., Kim J., Eom K., Oh S., Kim S., Kim G., Ahn S., Park K.H., Chung D., Lee H. microRNA-944 overexpression is a biomarker for poor prognosis of advanced cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:419. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5620-6. - DOI (V体育安卓版) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources

