Long Non-Coding RNAs: The Regulatory Mechanisms, Research Strategies, and Future Directions in Cancers
- PMID: 33392092
- PMCID: PMC7775490
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.598817
Long Non-Coding RNAs: The Regulatory Mechanisms, Research Strategies, and Future Directions in Cancers
Abstract
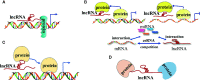
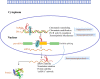
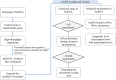
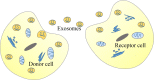
The development and application of whole genome sequencing technology has greatly broadened our horizons on the capabilities of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). LncRNAs are more than 200 nucleotides in length and lack protein-coding potential. Increasing evidence indicates that lncRNAs exert an irreplaceable role in tumor initiation, progression, as well as metastasis, and are novel molecular biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer patients. Furthermore, lncRNAs and the pathways they influence might represent promising therapeutic targets for a number of tumors. Here, we discuss the recent advances in understanding of the specific regulatory mechanisms of lncRNAs VSports手机版. We focused on the signal, decoy, guide, and scaffold functions of lncRNAs at the epigenetic, transcription, and post-transcription levels in cancer cells. Additionally, we summarize the research strategies used to investigate the roles of lncRNAs in tumors, including lncRNAs screening, lncRNAs characteristic analyses, functional studies, and molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs. This review will provide a short but comprehensive description of the lncRNA functions in tumor development and progression, thus accelerating the clinical implementation of lncRNAs as tumor biomarkers and therapeutic targets. .
Keywords: cancer; long non-coding RNA; mechanism of action; research strategies; therapeutic targets V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2020 Gao, Li, Li, Gao, Yang, Li, Liu and Fan V体育ios版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures (V体育平台登录)
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- JACOB F, MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol (1961) 3:318–56. 10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80072-7 - V体育平台登录 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, Zhu X, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science (2004) 306(5705):2242–6. 10.1126/science.1103388 - "VSports手机版" DOI - PubMed
-
- Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, Maeda N, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Sci (New York NY) (2005) 309(5740):1559. 10.1126/science.1112014 - "VSports最新版本" DOI - PubMed
-
- Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell (2009) 136(4):629–41. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006 - V体育2025版 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

