Tarloxotinib Is a Hypoxia-Activated Pan-HER Kinase Inhibitor Active Against a Broad Range of HER-Family Oncogenes
- PMID: 33355298
- PMCID: PMC7926264
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3555
Tarloxotinib Is a Hypoxia-Activated Pan-HER Kinase Inhibitor Active Against a Broad Range of HER-Family Oncogenes
Abstract
Purpose: Approved therapies for EGFR exon 20, ERBB2 mutations, and NRG1 fusions are currently lacking for non-small cell lung cancer and other cancers. Tarloxotinib is a prodrug that harnesses tumor hypoxia to generate high levels of a potent, covalent pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor, tarloxotinib-effector (tarloxotinib-E), within the tumor microenvironment. This tumor-selective delivery mechanism was designed to minimize the dose-limiting toxicities that are characteristic of systemic inhibition of wild-type EGFR VSports手机版. .
Experimental design: Novel and existing patient-derived cell lines and xenografts harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations, ERBB2 mutations and amplification, and NRG1 fusions were tested in vitro and in vivo with tarloxotinib to determine its impact on cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell signaling V体育安卓版. .
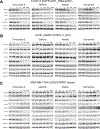
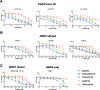
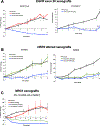
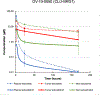
Results: Tarloxotinib-E inhibited cell signaling and proliferation in patient-derived cancer models in vitro by directly inhibiting phosphorylation and activation of EGFR, HER2, and HER2/HER3 heterodimers. In vivo, tarloxotinib induced tumor regression or growth inhibition in multiple murine xenograft models V体育ios版. Pharmacokinetic analysis confirmed markedly higher levels of tarloxotinib-E in tumor tissue than plasma or skin. Finally, a patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring an ERBB2 exon 20 p. A775_G776insYVMA mutation demonstrated a dramatic clinical response to tarloxotinib. .
Conclusions: Experimental data with tarloxotinib validate the novel mechanism of action of a hypoxia-activated prodrug in cancer models by concentrating active drug in the tumor versus normal tissue, and this activity can translate into clinical activity in patients. VSports最新版本.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research. V体育平台登录.
Conflict of interest statement
COI: AEB, AED, SS, and MRB, these authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

VSports最新版本 - References
-
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009;21(2):177–84 doi 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.010. - VSports - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;359(13):1367–80 doi 10.1056/NEJMra0802714. - DOI (VSports手机版) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2009;361(10):947–57 doi 10.1056/NEJMoa0810699. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15(2):213–22 doi 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70604-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Grants and funding
VSports手机版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports最新版本 - Research Materials
Miscellaneous

