Reversing the direction of drug transport mediated by the human multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein
- PMID: 33168729
- PMCID: PMC7703596
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016270117
Reversing the direction of drug transport mediated by the human multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein
Abstract
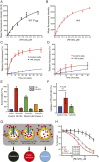
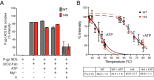
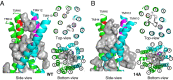
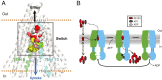
P-glycoprotein (P-gp), also known as ABCB1, is a cell membrane transporter that mediates the efflux of chemically dissimilar amphipathic drugs and confers resistance to chemotherapy in most cancers. Homologous transmembrane helices (TMHs) 6 and 12 of human P-gp connect the transmembrane domains with its nucleotide-binding domains, and several residues in these TMHs contribute to the drug-binding pocket. To investigate the role of these helices in the transport function of P-gp, we substituted a group of 14 conserved residues (seven in both TMHs 6 and 12) with alanine and generated a mutant termed 14A. Although the 14A mutant lost the ability to pump most of the substrates tested out of cancer cells, surprisingly, it acquired a new function. It was able to import four substrates, including rhodamine 123 (Rh123) and the taxol derivative flutax-1. Similar to the efflux function of wild-type P-gp, we found that uptake by the 14A mutant is ATP hydrolysis-, substrate concentration-, and time-dependent. Consistent with the uptake function, the mutant P-gp also hypersensitizes HeLa cells to Rh123 by 2- to 2. 5-fold VSports手机版. Further mutagenesis identified residues from both TMHs 6 and 12 that synergistically form a switch in the central region of the two helices that governs whether a given substrate is pumped out of or into the cell. Transforming P-gp or an ABC drug exporter from an efflux transporter into a drug uptake pump would constitute a paradigm shift in efforts to overcome cancer drug resistance. .
Keywords: ABC transporter; P-glycoprotein; drug transport; mechanism; multidrug resistance. V体育安卓版.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s) V体育ios版. Published by PNAS. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ambudkar S. V., Kimchi-Sarfaty C., Sauna Z. E., Gottesman M. M., P-glycoprotein: From genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 22, 7468–7485 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Eckford P. D., Sharom F. J., ABC efflux pump-based resistance to chemotherapy drugs. Chem. Rev. 109, 2989–3011 (2009). - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Gottesman M. M., Fojo T., Bates S. E., Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 48–58 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Juliano R. L., Ling V., A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455, 152–162 (1976). - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
"VSports最新版本" MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances (VSports)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

