Sirt1 during childhood is associated with microvascular function later in life
- PMID: 32330091
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC7311696
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00024.2020 (VSports)
Sirt1 during childhood is associated with microvascular function later in life
Abstract
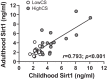
Microvascular dysfunction often precedes other age-related macrovascular conditions and predicts future cardiovascular risk. Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) has recently emerged as a protein that protects the vasculature and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases. We tested the hypothesis that lower Sirt1 during childhood is associated with a reduced microvascular function during adulthood. Thirty-four adults (34 ± 3 yr) from the Augusta Heart Study returned to participate in the present clinical observational study. Sirt1 was assessed in samples collected during both adulthood and participants' childhood (16 ± 3 yr), and data were divided based on childhood Sirt1 concentrations: <3 ng/dL (LowCS; n = 16) and ≥3 ng/dL (HighCS; n = 18). MVF was evaluated in all of the adults using laser-Doppler flowmetry coupled with three vascular reactivity tests: 1) local thermal hyperemia (LTH), 2) post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH), and 3) iontophoresis of acetylcholine (ACh). The hyperemic response to LTH was significantly (P ≤ 0. 044) lower in the LowCS than in the HighCS group. Similarly, the LowCS also exhibited an ameliorated (P ≤ 0. 045) response to the PORH test and lower (P ≤ 0. 008) vasodilation in response to iontophoresis of ACh when compared with the HighCS VSports手机版. Positive relationships were identified between childhood Sirt1 and all MVF reactivity tests (r≥0. 367, P ≤ 0. 004). Novel observations suggest that lower Sirt1 during childhood is associated with premature microvascular dysfunction in adulthood. These findings provide evidence that Sirt1 may play a critical role in microvascular function and have therapeutic potential for the prevention of age-associated vascular dysfunction in humans. NEW & NOTEWORTHY With a longitudinal cohort, novel observations from the present study demonstrate that individuals who had lower Sirt1 early in life exhibit premature microvascular dysfunction during adulthood and may be at higher risk to develop CVD. These results provide experimental evidence that Sirt1 may play an important role in microvascular function with age and represent a potential therapeutic target to prevent premature vascular dysfunction. .
Keywords: Sirt1; cardiovascular risk; childhood; microvascular function V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
V体育官网入口 - Figures


References
-
- Breitenstein A, Stein S, Holy EW, Camici GG, Lohmann C, Akhmedov A, Spescha R, Elliott PJ, Westphal CH, Matter CM, Lüscher TF, Tanner FC. Sirt1 inhibition promotes in vivo arterial thrombosis and tissue factor expression in stimulated cells. Cardiovasc Res 89: 464–472, 2011. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq339. - DOI (VSports) - PubMed
-
- Brunt VE, Minson CT. Cutaneous thermal hyperemia: more than skin deep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 111: 5–7, 2011. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00544.2011. - V体育安卓版 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen HZ, Wang F, Gao P, Pei JF, Liu Y, Xu TT, Tang X, Fu WY, Lu J, Yan YF, Wang XM, Han L, Zhang ZQ, Zhang R, Zou MH, Liu DP. Age-associated sirtuin 1 reduction in vascular smooth muscle links vascular senescence and inflammation to abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ Res 119: 1076–1088, 2016. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308895. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
"V体育官网" Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育ios版" Full Text Sources

