CDK12: an emerging therapeutic target for cancer
- PMID: 30104286
- PMCID: "VSports最新版本" PMC6242340
- DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205356
CDK12: an emerging therapeutic target for cancer
"VSports" Abstract
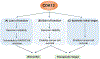
Cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12) belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) family of serine/threonine protein kinases that regulate transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes, thereby modulating multiple cellular functions. Early studies characterised CDK12 as a transcriptional CDK that complexes with cyclin K to mediate gene transcription by phosphorylating RNA polymerase II. CDK12 has been demonstrated to specifically upregulate the expression of genes involved in response to DNA damage, stress and heat shock VSports手机版. More recent studies have implicated CDK12 in regulating mRNA splicing, 3' end processing, pre-replication complex assembly and genomic stability during embryonic development. Genomic alterations in CDK12 have been detected in oesophageal, stomach, breast, endometrial, uterine, ovarian, bladder, colorectal and pancreatic cancers, ranging from 5% to 15% of sequenced cases. An increasing number of studies point to CDK12 inhibition as an effective strategy to inhibit tumour growth, and synthetic lethal interactions have been described with MYC, EWS/FLI and PARP/CHK1 inhibition. Herein, we discuss the present literature on CDK12 in cell function and human cancer, highlighting important roles for CDK12 as a clinical biomarker for treatment response and potential as an effective therapeutic target. .
Keywords: C-MYC oncogene; breast cancer; cancer genetics; cell biology; ovarian cancer. V体育安卓版.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2018 V体育ios版. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ. .
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CG and CJK are cofounders of and have ownership interests in SEngine Precision Medicine VSports最新版本. GYLL has no competing interests to declare.
Figures
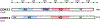


References
-
- Marques F, Moreau JL, Peaucellier G, et al. A new subfamily of high molecular mass CDC2-related kinases with PITAI/VRE motifs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;279(3):832–7. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Blazek D, Kohoutek J, Bartholomeeusen K, et al. The Cyclin K/Cdk12 complex maintains genomic stability via regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes. Genes Dev 2011;25(20):2158–72. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li X, Chatterjee N, Spirohn K, Boutros M, Bohmann D. Cdk12 Is A Gene-Selective RNA Polymerase II Kinase That Regulates a Subset of the Transcriptome, Including Nrf2 Target Genes. Sci Rep 2016;6:21455. - V体育安卓版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ko TK, Kelly E, Pines J. CrkRS: a novel conserved Cdc2-related protein kinase that colocalises with SC35 speckles. J Cell Sci 2001;114(Pt 14):2591–603. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育安卓版)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
