High expression of CD44v9 and xCT in chemoresistant hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential targets by sulfasalazine
- PMID: 29981246
- PMCID: PMC6125439
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13728
"V体育ios版" High expression of CD44v9 and xCT in chemoresistant hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential targets by sulfasalazine
Abstract
CD44v9 is expressed in cancer stem cells (CSC) and stabilizes the glutamate-cystine transporter xCT on the cytoplasmic membrane, thereby decreasing intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This mechanism confers ROS resistance to CSC and CD44v9-expressing cancer cells VSports手机版. The aims of the present study were to assess: (i) expression status of CD44v9 and xCT in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, including those derived from patients treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemoembolization (HAIC) therapy with cisplatin (CDDP); and (ii) whether combination of CDDP with sulfasalazine (SASP), an inhibitor of xCT, was more effective on tumor cells than CDDP alone by inducing ROS-mediated apoptosis. Twenty non-pretreated HCC tissues and 7 HCC tissues administered HAIC therapy with CDDP before surgical resection were subjected to immunohistochemistry analysis of CD44v9 and xCT expression. Human HCC cell lines HAK-1A and HAK-1B were used in this study; the latter was also used for xenograft experiments in nude mice to assess in vivo efficacy of combination treatment. CD44v9 positivity was significantly higher in HAIC-treated tissues (5/7) than in non-pretreated tissues (2/30), suggesting the involvement of CD44v9 in the resistance to HAIC. xCT was significantly expressed in poorly differentiated HCC tissues. Combination treatment effectively killed the CD44v9-harboring HAK-1B cells through ROS-mediated apoptosis and significantly decreased xenografted tumor growth. In conclusion, the xCT inhibitor SASP augmented ROS-mediated apoptosis in CDDP-treated HCC cells, in which the CD44v9-xCT system functioned. As CD44v9 is typically expressed in HAIC-resistant HCC cells, combination treatment with SASP with CDDP may overcome such drug resistance. .
Keywords: anticancer drug resistance; cancer stem cell; combinational therapy; oxidative stress; sphere formation V体育安卓版. .
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association V体育ios版. .
V体育官网入口 - Figures
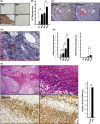
 P < 0.01; C, Limited number of
P < 0.01; C, Limited number of  P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. F, (left upper panel)
P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. F, (left upper panel)  P < 0.01
P < 0.01
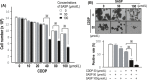
 P < 0.01). B, A synergistic inhibitory effect was seen even in sphere‐forming
P < 0.01). B, A synergistic inhibitory effect was seen even in sphere‐forming  P < 0.01
P < 0.01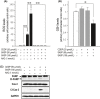
 P < 0.001. B, Decrease in intracellular glutathione (
P < 0.001. B, Decrease in intracellular glutathione ( P < 0.01. C, In western blotting, the apoptosis markers cleaved (Cl) poly (ADP‐ribose) polymerase (
P < 0.01. C, In western blotting, the apoptosis markers cleaved (Cl) poly (ADP‐ribose) polymerase (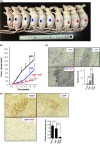
 P < 0.001). C, Consistent with the tumor growth inhibition, immunohistochemistry analysis of cleaved caspase‐3 showed significantly highest positivity in tumor tissues of mice treated with both
P < 0.001). C, Consistent with the tumor growth inhibition, immunohistochemistry analysis of cleaved caspase‐3 showed significantly highest positivity in tumor tissues of mice treated with both  means P < 0.001 or P < 0.01). D,
means P < 0.001 or P < 0.01). D,  P < 0.05;
P < 0.05;  P < 0.001)
P < 0.001)"VSports注册入口" References
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245‐1255. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Nagamatsu H, Sumie S, Niizeki T, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemoembolization therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: multicenter phase II study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;77:243‐250. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Nakano M, Tanaka M, Kuromatsu R, et al. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Cancer Med. 2015;4:1836‐1843. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- Pang RW, Poon RT. Cancer stem cell as a potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012;12:1081‐1094. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
"VSports手机版" Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网)
Other Literature Sources (V体育ios版)
Medical
Research Materials

