Resistance Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies in ROS1+ and ALK+ Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 29636358
- PMCID: VSports - PMC6050099
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2452
Resistance Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies in VSports - ROS1+ and ALK+ Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
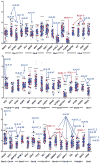
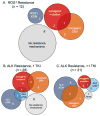
Purpose: Despite initial benefit from tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring ALK (ALK+) and ROS1 (ROS1+) gene fusions ultimately progress. Here, we report on the potential resistance mechanisms in a series of patients with ALK+ and ROS1+ NSCLC progressing on different types and/or lines of ROS1/ALK-targeted therapy. Experimental Design: We used a combination of next-generation sequencing (NGS), multiplex mutation assay, direct DNA sequencing, RT-PCR, and FISH to identify fusion variants/partners and copy-number gain (CNG), kinase domain mutations (KDM), and copy-number variations (CNVs) in other cancer-related genes. We performed testing on 12 ROS1+ and 43 ALK+ patients. Results: One of 12 ROS1+ (8%) and 15 of 43 (35%) ALK + patients harbored KDM. In the ROS1+ cohort, we identified KIT and β-catenin mutations and HER2-mediated bypass signaling as non-ROS1-dominant resistance mechanisms. In the ALK+ cohort, we identified a novel NRG1 gene fusion, a RET fusion, 2 EGFR, and 3 KRAS mutations, as well as mutations in IDH1, RIT1, NOTCH, and NF1 In addition, we identified CNV in multiple proto-oncogenes genes including PDGFRA, KIT, KDR, GNAS, K/HRAS, RET, NTRK1, MAP2K1, and others. Conclusions: We identified a putative TKI resistance mechanism in six of 12 (50%) ROS1 + patients and 37 of 43 (86%) ALK+ patients. Our data suggest that a focus on KDMs will miss most resistance mechanisms; broader gene testing strategies and functional validation is warranted to devise new therapeutic strategies for drug resistance VSports手机版. Clin Cancer Res; 24(14); 3334-47. ©2018 AACR. .
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest.
CEM- honoraria for Takeda, Guardant Health, DRC- honoraria from Takeda; RD – Pfizer speaker’s bureau and advisory board, Novartis, Roche, Ignyta – advisory board; RCD – AstraZeneca – advisory board, Guardant Health – honoraria, Pfizer – honoraria, Ignyta – advisory board and sponsored research grant, Takeda – advisory board, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals – advisory board, Abbott Molecular – remuneration for patent license, Rain Therapeutics – stock owner; PAB – consultant for Genentech and Pfizer; ATL – Abbott Molecular – remuneration for patent license; DTM, ATL, KG, KJ, LS, AD, AEB, KDD, MV-G, WTP, DLA - declare no potential conflicts of interest;
Figures
References
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131(6):1190–203. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.025. - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448(7153):561–6. doi: 10.1038/nature05945. - DOI (V体育2025版) - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Sharma S, Wigler M. Expression and rearrangement of the ROS1 gene in human glioblastoma cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1987;84(24):9270–4. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding (VSports)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

