MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion (V体育2025版)
- PMID: 28627030
- PMCID: "VSports最新版本" PMC5504333
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1110
MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion
Abstract
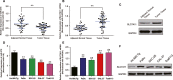
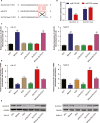
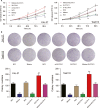
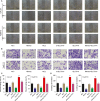
We aimed to detect the functions of miR-375/SLC7A11 axis on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell proliferation and invasion. Expression levels of miR-375 and SLC7A11 in OSCC tissues and cells were measured with RT-qPCR and western blot. Targeting site was predicted by TargetScan and confirmed by dual luciferase reporting assay. By way of manipulating the expression level of miR-375 and SLC7A11 in CAL-27 and Tca8113 cell lines, the cell biological abilities were evaluated. MTT, colony formation, Transwell, wound healing assays and flow cytometry were used to detect OSCC cell viability, proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis, respectively. MiR-375 was significantly downregulated in OSCC tissues and cells compared to adjacent tissue and normal oral cell line respectively while SLC7A11 was upregulated VSports手机版. Targeting relationship was verified by luciferase reporting assay, and miR-375 could effectively suppress SLC7A11 level in OSCC cells. Replenishing of miR-375 significantly repressed OSCC cell viability, proliferation, invasion and migration and induced cell apoptosis and G1/G0 arrest. Overexpression of SLC7A11 recovered those biological abilities in miR-375 upregulated cells. Collective data suggested that miR-375 served as a tumor suppressor via regulating SLC7A11. Replenishing of miR-375 or knockout of SLC7A11 could be therapeutically exploited. .
Keywords: OSCC; SLC7A11; miR-375 V体育安卓版. .
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd V体育ios版. .
Figures
"VSports" References
-
- Choi, S. , and Myers J. N.. 2008. Molecular pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: implications for therapy. J. Dent. Res. 87:14–32. - PubMed
-
- Zini, A. , Czerninski R., and Sgan‐Cohen H. D.. 2010. Oral cancer over four decades: epidemiology, trends, histology, and survival by anatomical sites. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 39:299–305. - "V体育官网" PubMed
-
- Forastiere, A. , Koch W., Trotti A., and Sidransky D.. 2001. Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 345:1890–1900. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Haddad, R. I. , and Shin D. M.. 2008. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 359:1143–1154. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育2025版)
Medical

