Effects of resveratrol on drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes, implications for cancer prevention
- PMID: 28596842
- PMCID: PMC5461649 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.294
Effects of resveratrol on drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes, implications for cancer prevention
Abstract
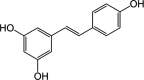
Resveratrol is a polyphenol found in grape skins and peanuts that has demonstrated many health benefits including protection against aging, cardiovascular and metabolic disease, neurological decline, and cancer. The anticancer properties of resveratrol have been attributed to a variety of mechanisms, including its general inhibition of phase I metabolism and induction of phase II metabolism VSports手机版. The effects of resveratrol on these enzymes, however, are still unclear, as in vitro evidence often contrasts with animal studies and clinical trials. Reasons for these variances could include the low bioavailability of resveratrol and the effects of resveratrol metabolites. Due to resveratrol's interactions with drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters, individuals concurrently taking pharmacological doses of resveratrol with other supplements or medications could potentially experience nutrient-drug interactions. This review summarizes the known effects of resveratrol and its main metabolites on drug metabolism in order to help characterize which populations might benefit from resveratrol for the prevention of cancer, as well as those that may need to avoid supplementation due to potential drug interactions. .
Keywords: Chemoprevention; cytochrome P450; resveratrol V体育安卓版. .
Figures (V体育平台登录)
References (VSports app下载)
-
- Aires V, Limagne E, Cotte AK, Latruffe N, Ghiringhelli F, Delmas D (2013). Resveratrol metabolites inhibit human metastatic colon cancer cells progression and synergize with chemotherapeutic drugs to induce cell death. Mol Nutr Food Res 57: 1170–1181. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Alfaras I, Pérez M, Juan ME, Merino G, Prieto JG, Planas JM, et al. (2010). Involvement of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP1/ABCG2) in the bioavailability and tissue distribution of trans‐ resveratrol in knockout mice. J Agric Food Chem 58: 4523–4528. - PubMed (VSports在线直播)
-
- Ali MHH, Messiha BAS, Abdel‐Latif HA‐T (2015). Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid, resveratrol, and N‐acetylcysteine on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Pharm Biol 54: 1198–1208. Taylor & Francis. - PubMed
-
- Bastianetto S, Ménard C, Quirion R (2015). Neuroprotective action of resveratrol. BBA Mol Basis Dis 1852: 1195–1201.Elsevier B.V. - PubMed
-
- Bedada SK, Nearati P (2015). Effect of resveratrol on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in healthy human volunteers. Phyther Res 29: 701–706. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育安卓版" Other Literature Sources

