Measuring shear-wave speed with point shear-wave elastography and MR elastography: a phantom study
- PMID: 28057657
- PMCID: PMC5223661
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013925
Measuring shear-wave speed with point shear-wave elastography and MR elastography: a phantom study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare shear-wave speed (SWS) measured by ultrasound-based point shear-wave elastography (pSWE) and MR elastography (MRE) on phantoms with a known shear modulus, and to assess method validity and variability VSports手机版. .
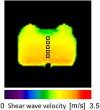
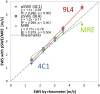
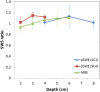
Methods: 5 homogeneous phantoms of different stiffnesses were made. Shear modulus was measured by a rheometer, and this value was used as the standard. 10 SWS measurements were obtained at 4 different depths with 1. 0-4. 5 MHz convex (4C1) and 4. 0-9. 0 MHz linear (9L4) transducers using pSWE. MRE was carried out once per phantom, and SWSs at 5 different depths were obtained V体育安卓版. These SWSs were then compared with those from a rheometer using linear regression analyses. .
Results: SWSs obtained with both pSWE as well as MRE had a strong correlation with those obtained by a rheometer (R2>0. 97). The relative difference in SWS between the procedures was from -25. 2% to 25. 6% for all phantoms, and from -8. 1% to 6. 9% when the softest and hardest phantoms were excluded. Depth dependency was noted in the 9L4 transducer of pSWE and MRE V体育ios版. .
Conclusions: SWSs from pSWE and MRE showed a good correlation with a rheometer-determined SWS. Although based on phantom studies, SWSs obtained with these methods are not always equivalent, the measurement can be thought of as reliable and these SWSs were reasonably close to each other for the middle range of stiffness within the measurable range. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: acoustic radiation force impulse; elastography; rheometer; shear wave V体育平台登录. .
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www. bmj VSports注册入口. com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/. .
Conflict of interest statement (V体育官网)
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S et al. . Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology 2009;252:595–604. 10.1148/radiol.2523081928 - DOI (V体育官网入口) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
V体育官网入口 - Medical
