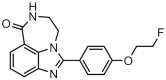
[(18)F]FluorThanatrace uptake as a marker of PARP1 expression and activity in breast cancer (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 27069769
- PMCID: PMC4749508
[(18)F]FluorThanatrace uptake as a marker of PARP1 expression and activity in breast cancer (VSports app下载)
Abstract
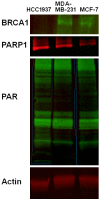
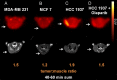
The nuclear enzyme PARP1 plays a central role in sensing DNA damage and facilitating repair. Tumors with BRCA1/2 mutations are highly dependent on PARP1 as an alternative mechanism for DNA repair, and PARP inhibitors generate synthetic lethality in tumors with BRCA mutations, resulting in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Zhou et al. recently synthesized an (18)F-labeled PARP1 inhibitor ([(18)F]FluorThanatrace) for PET, and demonstrated high specific tracer uptake in a xenograft model of breast cancer [1]. In the current study, we characterize the level of baseline PARP expression and activity across multiple human breast cancer cell lines, including a BRCA1 mutant line. PARP expression and activity, as measured by levels of PAR and PARP1, is correlated with in vitro [(18)F]FluorThanatrace binding as well as tracer uptake on PET in a xenograft model of breast cancer. Radiotracer uptake in genetically-engineered mouse fibroblasts indicates [(18)F]FluorThanatrace is selective for PARP1 versus other PARP enzymes. This motivates further studies of [(18)F]FluorThanatrace as an in vivo measure of PARP1 expression and activity in patients who would benefit from PARP inhibitor therapy VSports手机版. .
Keywords: BRCA mutation; PARP1; breast cancer. V体育安卓版.
Figures (V体育2025版)

References (V体育官网)
-
- Zhou D, Chu W, Xu J, Jones LA, Peng X, Li S, Chen DL, Mach RH. Synthesis, [18F] radiolabeling, and evaluation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) inhibitors for in vivo imaging of PARP-1 using positron emission tomography. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014;22:1700–1707. - VSports手机版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hassa PO, Hottiger MO. The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3046–3082. - PubMed
-
- Kameshita I, Matsuda Z, Taniguchi T, Shizuta Y. Poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase. Separation and identification of three proteolytic fragments as the substrate-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, and the automodification domain. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:4770–4776. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Tangutoori S, Baldwin P, Sridhar S. PARP inhibitors: A new era of targeted therapy. Maturitas. 2015;81:5–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources (V体育平台登录)
Full Text Sources (VSports)
"VSports在线直播" Other Literature Sources
VSports手机版 - Miscellaneous
