Transcriptomic Profile of Whole Blood Cells from Elderly Subjects Fed Probiotic Bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ATCC 53103 (LGG) in a Phase I Open Label Study
- PMID: 26859761
- PMCID: PMC4747532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147426
"VSports注册入口" Transcriptomic Profile of Whole Blood Cells from Elderly Subjects Fed Probiotic Bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ATCC 53103 (LGG) in a Phase I Open Label Study
Abstract
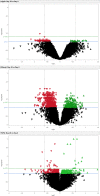
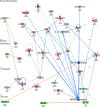
We examined gene expression of whole blood cells (WBC) from 11 healthy elderly volunteers participating on a Phase I open label study before and after oral treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-ATCC 53103 (LGG)) using RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq). Elderly patients (65-80 yrs) completed a clinical assessment for health status and had blood drawn for cellular RNA extraction at study admission (Baseline), after 28 days of daily LGG treatment (Day 28) and at the end of the study (Day 56) after LGG treatment had been suspended for 28 days. Treatment compliance was verified by measuring LGG-DNA copy levels detected in host fecal samples. Normalized gene expression levels in WBC RNA were analyzed using a paired design built within three analysis platforms (edgeR, DESeq2 and TSPM) commonly used for gene count data analysis. From the 25,990 transcripts detected, 95 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected in common by all analysis platforms with a nominal significant difference in gene expression at Day 28 following LGG treatment (FDR<0. 1; 77 decreased and 18 increased). With a more stringent significance threshold (FDR<0. 05), only two genes (FCER2 and LY86), were down-regulated more than 1. 5 fold and met the criteria for differential expression across two analysis platforms. The remaining 93 genes were only detected at this threshold level with DESeq2 platform. Data analysis for biological interpretation of DEGs with an absolute fold change of 1. 5 revealed down-regulation of overlapping genes involved with Cellular movement, Cell to cell signaling interactions, Immune cell trafficking and Inflammatory response VSports手机版. These data provide evidence for LGG-induced transcriptional modulation in healthy elderly volunteers because pre-treatment transcription levels were restored at 28 days after LGG treatment was stopped. To gain insight into the signaling pathways affected in response to LGG treatment, DEG were mapped using biological pathways and genomic data mining packages to indicate significant biological relevance. .
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials. gov NCT01274598. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures (VSports注册入口)

VSports注册入口 - References
-
- Chiba E, Tomosada Y, Vizoso-Pinto MG, Salva S, Takahashi T, Tsukida K, et al. (2013) Immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus improves resistance of infant mice against respiratory syncytial virus infection. Int Immunopharmacol 17: 373–382. 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.06.024 - V体育官网 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miettinen M, Pietila TE, Kekkonen RA, Kankainen M, Latvala S, Pirhonen J, et al. (2012) Nonpathogenic Lactobacillus rhamnosus activates the inflammasome and antiviral responses in human macrophages. Gut Microbes 3: 510–522. 10.4161/gmic.21736 - "V体育平台登录" DOI - PMC - PubMed
V体育2025版 - Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
"VSports app下载" MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Associated data (V体育安卓版)
Grants and funding
"V体育官网入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育2025版)
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

