Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis
- PMID: 26517407
- PMCID: PMC4851925 (V体育官网)
- DOI: "VSports app下载" 10.1002/ejp.818
"V体育安卓版" Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis
Abstract
Background: Current arthritis treatments often have side-effects attributable to active compounds as well as route of administration VSports手机版. Cannabidiol (CBD) attenuates inflammation and pain without side-effects, but CBD is hydrophobic and has poor oral bioavailability. Topical drug application avoids gastrointestinal administration, first pass metabolism, providing more constant plasma levels. .
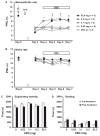
Methods: This study examined efficacy of transdermal CBD for reduction in inflammation and pain, assessing any adverse effects in a rat complete Freund's adjuvant-induced monoarthritic knee joint model. CBD gels (0. 6, 3. 1, 6. 2 or 62. 3 mg/day) were applied for 4 consecutive days after arthritis induction. Joint circumference and immune cell invasion in histological sections were measured to indicate level of inflammation. Paw withdrawal latency (PWL) in response to noxious heat stimulation determined nociceptive sensitization, and exploratory behaviour ascertained animal's activity level V体育安卓版. .
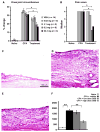
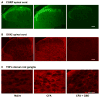
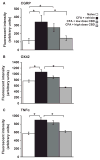
Results: Measurement of plasma CBD concentration provided by transdermal absorption revealed linearity with 0. 6-6. 2 mg/day doses. Transdermal CBD gel significantly reduced joint swelling, limb posture scores as a rating of spontaneous pain, immune cell infiltration and thickening of the synovial membrane in a dose-dependent manner. PWL recovered to near baseline level. Immunohistochemical analysis of spinal cord (CGRP, OX42) and dorsal root ganglia (TNFα) revealed dose-dependent reductions of pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Results showed 6. 2 and 62 mg/day were effective doses. Exploratory behaviour was not altered by CBD indicating limited effect on higher brain function. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: These data indicate that topical CBD application has therapeutic potential for relief of arthritis pain-related behaviours and inflammation without evident side-effects VSports最新版本. .
© 2015 European Pain Federation - EFIC®
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Akopian AN. Regulation of nociceptive transmission at the periphery via TRPA1-TRPV1 interactions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Ruparel NB, Patwardhan A, Hargreaves KM. Cannabinoids desensitize capsaicin and mustard oil responses in sensory neurons via TRPA1 activation. J Neurosci. 2008;8:1064–1075. - VSports手机版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Begg M, Pacher P, Batkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Offertaler L, Mo FM, Liu J, Kunos G. Evidence for novel cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;106:133–145. - PubMed
-
- Berckmans RJ, Nieuwland R, Kraan MC, Schaap MC, Pots D, Smeets TJ, Sturk A, Tak PP. Synovial microparticles from arthritic patients modulate chemokine and cytokine release by synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R536–R544. - VSports在线直播 - PMC - PubMed
V体育官网 - MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

