VSports最新版本 - Long non-coding RNA expression profiles predict metastasis in lymph node-negative breast cancer independently of traditional prognostic markers
- PMID: 25887545
- PMCID: PMC4416310
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-015-0557-4
V体育2025版 - Long non-coding RNA expression profiles predict metastasis in lymph node-negative breast cancer independently of traditional prognostic markers
"V体育官网入口" Abstract
Introduction: Patients with clinically and pathologically similar breast tumors often have very different outcomes and treatment responses VSports手机版. Current prognostic markers allocate the majority of breast cancer patients to the high-risk group, yielding high sensitivities in expense of specificities below 20%, leading to considerable overtreatment, especially in lymph node-negative patients. Seventy percent would be cured by surgery and radiotherapy alone in this group. Thus, precise and early indicators of metastasis are highly desirable to reduce overtreatment. Previous prognostic RNA-profiling studies have only focused on the protein-coding part of the genome, however the human genome contains thousands of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and this unexplored field possesses large potential for identification of novel prognostic markers. .
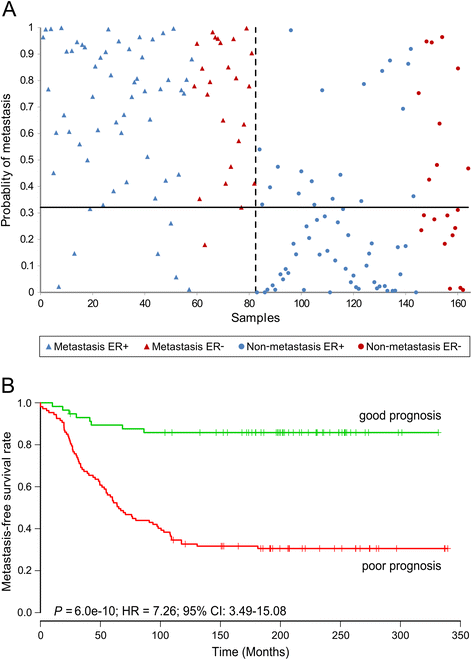
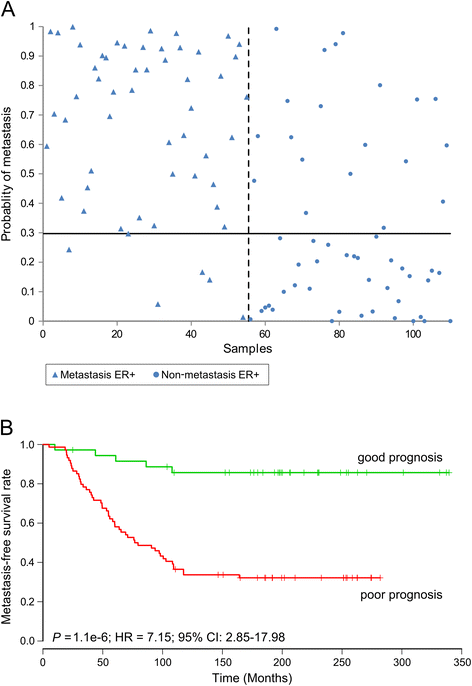
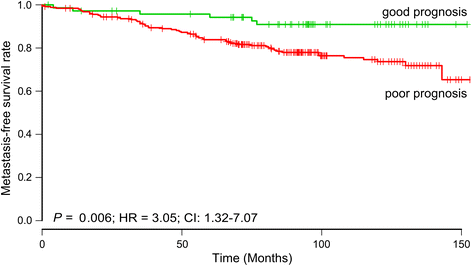
Methods: We evaluated lncRNA microarray data from 164 primary breast tumors from adjuvant naïve patients with a mean follow-up of 18 years V体育安卓版. Eighty two patients who developed detectable distant metastasis were compared to 82 patients where no metastases were diagnosed. For validation, we determined the prognostic value of the lncRNA profiles by comparing the ability of the profiles to predict metastasis in two additional, previously-published, cohorts. .
Results: We showed that lncRNA profiles could distinguish metastatic patients from non-metastatic patients with sensitivities above 90% and specificities of 64-65%. Furthermore; classifications were independent of traditional prognostic markers and time to metastasis V体育ios版. .
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating the prognostic potential of lncRNA profiles. Our study suggest that lncRNA profiles provide additional prognostic information and may contribute to the identification of early breast cancer patients eligible for adjuvant therapy, as well as early breast cancer patients that could avoid unnecessary systemic adjuvant therapy. This study emphasizes the potential role of lncRNAs in breast cancer prognosis VSports最新版本. .
Figures
References
-
- Veer LJ V ’t, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AAM, Mao M, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002;415:530–6. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de RM, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
VSports app下载 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

