Antipyretic therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis: an interaction with body temperature
- PMID: 25822614
- PMCID: PMC4378844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121919 (VSports app下载)
Antipyretic therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis: an interaction with body temperature
Abstract
Background and objective: The effect of antipyretic therapy on mortality in patients with sepsis remains undetermined. The present study aimed to investigate the role of antipyretic therapy in ICU patients with sepsis by using a large clinical database. VSports手机版.
Methods: The multiparameter intelligent monitoring in intensive care II (MIMIC- II) database was employed for the study. Adult patients with sepsis were included for analysis. Antipyretic therapy included antipyretic medication and external cooling. Multivariable model with interaction terms were employed to explore the association of antipyretic therapy and mortality risk. V体育安卓版.
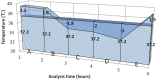
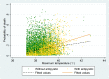
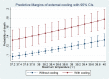
Main results: A total of 15,268 patients fulfilled inclusion criteria and were included in the study. In multivariable model by treating temperature as a continuous variable, there was significant interaction between antipyretic therapy and the maximum temperature (Tmax). While antipyretic therapy had no significant effect on mortality in low temperature quintiles, antipyretic therapy was associated with increased risk of death in the quintile with body temperature >39°C (OR: 1. 29, 95% CI: 1. 04-1. 61). V体育ios版.
Conclusion: Our study shows that there is no beneficial effect on reducing mortality risk with the use of antipyretic therapy in ICU patients with sepsis. External cooling may even be harmful in patients with sepsis. VSports最新版本.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
VSports注册入口 - References
"VSports注册入口" Publication types
- "VSports手机版" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
V体育安卓版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

