Objective measurement and clinical significance of TILs in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 25650315
- PMCID: PMC4565530
- DOI: "V体育ios版" 10.1093/jnci/dju435
Objective measurement and clinical significance of TILs in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are usually measured using subjective methods. Studies suggest that TIL subtypes have independent roles in cancer and that they could support the use of novel immunostimulatory therapies. We simultaneously measured TIL subtypes in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples using objective methods and determined their relationship with clinico-pathologic characteristics and survival. VSports手机版.
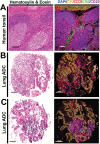
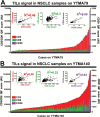
Methods: Using multiplexed quantitative fluorescence (QIF), we measured the levels of CD3, CD8, and CD20 in 552 NSCLC from two independent collections represented in tissue microarrays (YTMA79, n = 202 and YTMA140, n = 350). The level of TILs was obtained in different tumor compartments using cytokeratin stain to define tumor cells and 4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole. Association of TILs with clinical parameters was determined using univariate and multivariable analyses. All statistical tests were two-sided. V体育安卓版.
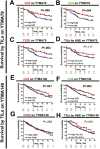
Results: In both NSCLC collections there was a low correlation between the three TIL markers (linear regression coefficients (R(2)) = 0. 19-0. 22, P < . 001 for YTMA79 and R(2) = 0. 23-0. 32, P < . 001 for YTMA140). No consistent association between the level of TIL subtypes and age, sex, smoking history, tumor size, stage, and histology type was found. In univariate analysis, an elevated CD3 or CD8 signal was statistically significantly associated with longer survival in both collections. However, only CD8 was independent from age, tumor size, histology, and stage in multivariable analysis V体育ios版. High CD20 was associated with longer survival in the YTMA79 cohort. .
Conclusions: Increased levels of CD3 and CD8 + TILs are associated with better outcome in NSCLC, but only CD8 is independent from other prognostic variables. Objective measurement of TIL subpopulations could be useful to predict response or evaluate the local immune effect of anticancer immune checkpoint inhibitors. VSports最新版本.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@www.qiuluzeuv.cn. V体育平台登录.
Figures
References
-
- Fridman WH, Pagès F, Sautès-Fridman C, et al. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):298–306. - PubMed
-
- Horne ZD, Jack R, Gray ZT, et al. Increased levels of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with improved recurrence-free survival in stage 1A non-small-cell lung cancer. J Surg Res. 2011;171(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Kilic A, Landreneau RJ, Luketich JD, et al. Density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlates with disease recurrence and survival in patients with large non-small-cell lung cancer tumors. J Surg Res. 2011;167(2):207–210. - PubMed
-
- Velcheti V, Schalper KA, Carvajal DE, et al. Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lab Invest. 2014;94(1):107–116. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhuang X, Xia X, Wang C, et al. A high number of CD8+ T cells infiltrated in NSCLC tissues is associated with a favorable prognosis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2010;18(1):24–28. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
MeSH terms (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
"VSports注册入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (VSports在线直播)
Research Materials

