Global metabolic profiling of infection by an oncogenic virus: KSHV induces and requires lipogenesis for survival of latent infection
- PMID: 22916018
- PMCID: "V体育官网入口" PMC3420960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002866
V体育平台登录 - Global metabolic profiling of infection by an oncogenic virus: KSHV induces and requires lipogenesis for survival of latent infection
"VSports app下载" Abstract
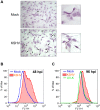
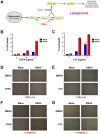
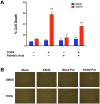
Like cancer cells, virally infected cells have dramatically altered metabolic requirements. We analyzed global metabolic changes induced by latent infection with an oncogenic virus, Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). KSHV is the etiologic agent of Kaposi's Sarcoma (KS), the most common tumor of AIDS patients. Approximately one-third of the nearly 200 measured metabolites were altered following latent infection of endothelial cells by KSHV, including many metabolites of anabolic pathways common to most cancer cells. KSHV induced pathways that are commonly altered in cancer cells including glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway, amino acid production and fatty acid synthesis. Interestingly, over half of the detectable long chain fatty acids detected in our screen were significantly increased by latent KSHV infection VSports手机版. KSHV infection leads to the elevation of metabolites involved in the synthesis of fatty acids, not degradation from phospholipids, and leads to increased lipid droplet organelle formation in the infected cells. Fatty acid synthesis is required for the survival of latently infected endothelial cells, as inhibition of key enzymes in this pathway led to apoptosis of infected cells. Addition of palmitic acid to latently infected cells treated with a fatty acid synthesis inhibitor protected the cells from death indicating that the products of this pathway are essential. Our metabolomic analysis of KSHV-infected cells provides insight as to how oncogenic viruses can induce metabolic alterations common to cancer cells. Furthermore, this analysis raises the possibility that metabolic pathways may provide novel therapeutic targets for the inhibition of latent KSHV infection and ultimately KS tumors. .
VSports注册入口 - Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Warburg O (1956) On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 124: 269–270. - PubMed
-
- Coleman MC, Asbury CR, Daniels D, Du J, Aykin-Burns N, et al. (2008) 2-deoxy-D-glucose causes cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and radiosensitization in pancreatic cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 44: 322–331. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Hu YP, Savaraj N, Priebe W, Lampidis TJ (2001) Hypersensitization of tumor cells to glycolytic inhibitors. Biochemistry (Mosc) 40: 5542–5547. - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava V, Mishra AK, Dwarakanath BS, Ravindranath T (2006) Enhancement of radionuclide induced cytotoxicity by 2-deoxy-D-glucose in human tumor cell lines. J Cancer Res Ther 2: 57–64. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
"VSports在线直播" Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Grants and funding
V体育平台登录 - LinkOut - more resources
"VSports在线直播" Full Text Sources
Medical

