Phenolic compounds in Brassica vegetables
- PMID: 21193847
- PMCID: PMC6259264 (V体育2025版)
- DOI: V体育平台登录 - 10.3390/molecules16010251
Phenolic compounds in Brassica vegetables
Abstract
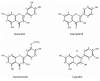
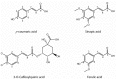
Phenolic compounds are a large group of phytochemicals widespread in the plant kingdom VSports手机版. Depending on their structure they can be classified into simple phenols, phenolic acids, hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and flavonoids. Phenolic compounds have received considerable attention for being potentially protective factors against cancer and heart diseases, in part because of their potent antioxidative properties and their ubiquity in a wide range of commonly consumed foods of plant origin. The Brassicaceae family includes a wide range of horticultural crops, some of them with economic significance and extensively used in the diet throughout the world. The phenolic composition of Brassica vegetables has been recently investigated and, nowadays, the profile of different Brassica species is well established. Here, we review the significance of phenolic compounds as a source of beneficial compounds for human health and the influence of environmental conditions and processing mechanisms on the phenolic composition of Brassica vegetables. .
Figures
References (V体育平台登录)
-
- Podsedek A. Natural antioxidants and antioxidant capacity of Brassica vegetables: A review. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2007;40:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2005.07.023. - DOI
-
- Jahangir M., Kim H.K., Choi Y.H., Verpoorte R. Health-Affecting Compounds in Brassicaceae. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009;8:31–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-4337.2008.00065.x. - DOI
-
- Crozier A., Jaganath I.B., Clifford M.N. Phenols, polyphenols and tannins: An overview. In: Crozier A., Clifford M., Ashihara H., editors. Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet. Blackwell; Oxford, UK: 2006. pp. 1–24.
-
- Pereira D.M., Valentao P., Pereira J.A., Andrade P.B. Phenolics: From Chemistry to Biology. Molecules. 2009;14:2202–2211. doi: 10.3390/molecules14062202. - DOI
-
- Hollman P.C.H., Arts I.C.W. Flavonols, flavones and flavanols - nature, occurrence and dietary burden. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000;80:1081–1093. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(20000515)80:7<1081::AID-JSFA566>3.0.CO (V体育ios版);2-G. - DOI
Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
"V体育ios版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育平台登录)