p53-Reactivating small molecules induce apoptosis and enhance chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 21109480
- PMCID: "VSports注册入口" PMC3032831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2010.10.011
p53-Reactivating small molecules induce apoptosis and enhance chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (V体育官网入口)
Abstract
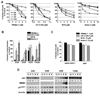
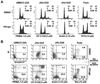
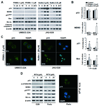
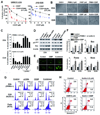
We evaluate whether p53-reactivating (p53RA) small molecules induce p53-dependent apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a question that has not been previously addressed in head and neck cancer. PRIMA-1, CP-31398, RITA, and nutlin-3 were tested in four human HNSCC cell lines differing in TP53 status. Cell growth, viability, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis after treatment with p53RA small molecules individually or in combination with chemotherapeutic agents were assessed. Prominent p53 reactivation was observed in mutant TP53-bearing tumor cell lines treated with PRIMA-1 or CP-31398, and in wild-type TP53-bearing cell lines treated with nutlin-3 VSports手机版. Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by p53RA small molecules were associated with upregulation of p21 and BAX, and cleavage of caspase-3. Nutlin-3 showed maximal growth suppression in tumor cells showing MDM2-dependent p53 degradation. High-dose treatment with p53RA small molecules also induced apoptosis in cell lines independent of p53 or MDM2 expression. In combination therapy, p53RA small molecules enhanced the anti-tumor activity of cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, and erlotinib against HNSCC cells. The p53RA small molecules effectively restored p53 tumor-suppressive function in HNSCCs with mutant or wild-type TP53. The p53RA agents may be clinically useful against HNSCC, in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. .
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. V体育安卓版.
V体育平台登录 - Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Levine AJ. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell. 1997;88(3):323–331. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Lu X., q Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(8):594–604. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Prives C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137(3):413–431. - PubMed
-
- Green DR, Kroemer G. Cytoplasmic functions of the tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 2009;458(7242):1127–1130. - PMC (VSports手机版) - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, Eeles R, Hollstein M, Khan MA, Harris CC, Hainaut P. The IARC TP53 database: new online mutation analysis and recommendations to users. Hum Mutat. 2002;19(6):607–614. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
Publication types
"VSports手机版" MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
V体育安卓版 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Medical
V体育官网入口 - Research Materials
Miscellaneous

