"V体育ios版" Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells
- PMID: 20397301
- PMCID: PMC2925492
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00664.x
Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Naringin, a flavanone glycoside in citrus fruits, has been recently reported to stimulate bone formation in vitro and in vivo. The present study was designed to determine if naringin could exert oestrogen-like protective actions in bone VSports手机版. .
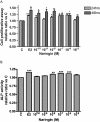
Experimental approach: Young C57/BL6J mice were ovariectomized (OVX) and treated orally with naringin (0. 2 or 0. 4 mg*g(-1)*day(-1)), 17beta-oestradiol (2 microg*g(-1)*day(-1)) or its vehicle for 6 weeks. Bone mineral densities (BMD) and polar stresss-train index (SSI) were measured by peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Rat osteoblast-like UMR-106 cells were co-incubated with the oestrogen receptor (ER) antagonist ICI 182780 to determine if the effects of naringin on osteoblastic functions were ER dependent. Functional transactivation of ERalpha and ERbeta as well as ERalpha phosphorylation by naringin were also studied V体育安卓版. .
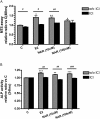
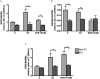
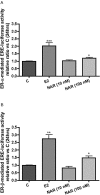
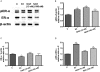
Key results: Naringin at 0. 4 mg*g(-1)*day(-1) increased BMD at trabecular-rich bone in OVX mice. Naringin (at both doses) significantly increased SSI at distal femur and lumbar spine and increased biomechanical strength (ultimate load and energy for breaking) at tibia diaphysis in OVX mice V体育ios版. The stimulatory effects of naringin on osteoblastic functions could be abolished by co-incubation with ICI 182780 in UMR-106 cells. Naringin failed to stimulate ERalpha- or ERbeta-mediated oestrogen response element-dependent luciferase activity but could significantly induce ERalpha phosphorylation at serine 118, in UMR-106 cells. .
Conclusions and implications: Naringin was effective in protecting against OVX-induced bone loss in mice and its actions might be mediated through ligand-independent activation of ER in osteoblastic cells VSports最新版本. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures
References
-
- Benavente-Garcia O, Castillo J. Update on uses and properties of citrus flavonoids: new findings in anticancer, cardiovascular, and anti-inflammatory activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:6185–6205. - PubMed
-
- Bjornstrom L, Sjoberg M. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:833–842. - PubMed
-
- Bord S, Ireland DC, Beavan SR, Compston JE. The effects of estrogen on osteoprotegerin, RANKL, and estrogen receptor expression in human osteoblasts. Bone. 2003;32:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Bunone G, Briand PA, Miksicek RJ, Picard D. Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1996;15:2174–2183. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
"VSports app下载" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports手机版)

