"V体育ios版" A logistic regression model based on the national mammography database format to aid breast cancer diagnosis
- PMID: 19304723
- PMCID: PMC2661033
- DOI: "V体育官网入口" 10.2214/AJR.07.3345
V体育ios版 - A logistic regression model based on the national mammography database format to aid breast cancer diagnosis
"V体育官网入口" Erratum in
- AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009 May;192(5):1167
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of our study was to create a breast cancer risk estimation model based on the descriptors of the National Mammography Database using logistic regression that can aid in decision making for the early detection of breast cancer VSports手机版. .
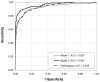
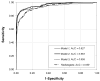
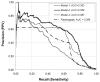
Materials and methods: We created two logistic regression models based on the mammography features and demographic data for 62,219 consecutive mammography records from 48,744 studies in 18,269 [corrected] patients reported using the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) lexicon and the National Mammography Database format between April 5, 1999 and February 9, 2004. State cancer registry outcomes matched with our data served as the reference standard. The probability of cancer was the outcome in both models. Model 2 was built using all variables in Model 1 plus radiologists' BI-RADS assessment categories. We used 10-fold cross-validation to train and test the model and to calculate the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (A(z)) to measure the performance. Both models were compared with the radiologists' BI-RADS assessments. V体育安卓版.
Results: Radiologists achieved an A(z) value of 0 V体育ios版. 939 +/- 0. 011. The A(z) was 0. 927 +/- 0. 015 for Model 1 and 0. 963 +/- 0. 009 for Model 2. At 90% specificity, the sensitivity of Model 2 (90%) was significantly better (p < 0. 001) than that of radiologists (82%) and Model 1 (83%). At 85% sensitivity, the specificity of Model 2 (96%) was significantly better (p < 0. 001) than that of radiologists (88%) and Model 1 (87%). .
Conclusion: Our logistic regression model can effectively discriminate between benign and malignant breast disease and can identify the most important features associated with breast cancer VSports最新版本. .
Figures
References
-
- Kopans DB. The positive predictive value of mammography. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1992;158:521–526. - PubMed
-
- Kerlikowske K, Grady D, Barclay J, et al. Variability and accuracy in mammographic interpretation using the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data Systems. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1998;90:1801–1809. - PubMed
-
- Elmore JG, Miglioretti DL, Reisch LM, et al. Screening Mammograms by Community Radiologists: Variability in False-Positive Rates. JNCI Cancer Spectrum. 2002;94:1373–1380. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Miglioretti DL, Smith-Bindman R, Abraham L, et al. Radiologist Characteristics Associated With Interpretive Performance of Diagnostic Mammography. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2007;99:1854. - PMC (VSports) - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

