WNT1-inducible signaling protein-1 mediates pulmonary fibrosis in mice and is upregulated in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 19287097
- PMCID: PMC2662540
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33950
WNT1-inducible signaling protein-1 mediates pulmonary fibrosis in mice and is upregulated in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
V体育官网 - Abstract
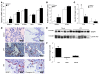
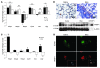
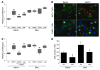
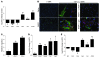
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by distorted lung architecture and loss of respiratory function. Enhanced (myo)fibroblast activation, ECM deposition, and alveolar epithelial type II (ATII) cell dysfunction contribute to IPF pathogenesis. However, the molecular pathways linking ATII cell dysfunction with the development of fibrosis are poorly understood VSports手机版. Here, we demonstrate, in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis, increased proliferation and altered expression of components of the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in ATII cells. Further analysis revealed that expression of WNT1-inducible signaling protein-1 (WISP1), which is encoded by a WNT target gene, was increased in ATII cells in both a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis and patients with IPF. Treatment of mouse primary ATII cells with recombinant WISP1 led to increased proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), while treatment of mouse and human lung fibroblasts with recombinant WISP1 enhanced deposition of ECM components. In the mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis, neutralizing mAbs specific for WISP1 reduced the expression of genes characteristic of fibrosis and reversed the expression of genes associated with EMT. More importantly, these changes in gene expression were associated with marked attenuation of lung fibrosis, including decreased collagen deposition and improved lung function and survival. Our study thus identifies WISP1 as a key regulator of ATII cell hyperplasia and plasticity as well as a potential therapeutic target for attenuation of pulmonary fibrosis. .
Figures
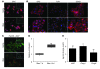
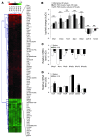
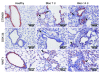
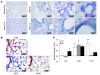
References
-
- American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society. . American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Selman M., King T.E., Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
-
- Thannickal V.J., Toews G.B., White E.S., Lynch J.P., 3rd, Martinez F.J. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004;55:395–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.55.091902.103810. - V体育官网入口 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noble P.W., Homer R.J. Back to the future: historical perspective on the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005;33:113–120. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.F301. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
VSports最新版本 - MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports - Actions
VSports注册入口 - Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports最新版本)
Medical
Research Materials

