"V体育ios版" Nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 during S phase inhibits Cul4-dependent Cdt1 proteolysis and triggers p53-dependent DNA rereplication
- PMID: 18006686
- PMCID: PMC2049193 (V体育平台登录)
- DOI: "V体育平台登录" 10.1101/gad.1586007
Nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 during S phase inhibits Cul4-dependent Cdt1 proteolysis and triggers p53-dependent DNA rereplication (V体育2025版)
"VSports" Abstract
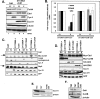
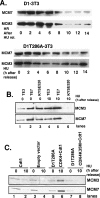
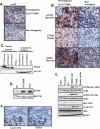
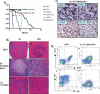
Deregulation of cyclin D1 occurs in numerous human cancers through mutations, alternative splicing, and gene amplification VSports手机版. Although cancer-derived cyclin D1 mutants are potent oncogenes in vitro and in vivo, the mechanisms whereby they contribute to neoplasia are poorly understood. We now provide evidence derived from both mouse models and human cancer-derived cells revealing that nuclear accumulation of catalytically active mutant cyclin D1/CDK4 complexes triggers DNA rereplication, resulting from Cdt1 stabilization, which in turn triggers the DNA damage checkpoint and p53-dependent apoptosis. Loss of p53 through mutations or targeted deletion results in increased genomic instability and neoplastic growth. Collectively, the data presented reveal mechanistic insights into how uncoupling of critical cell cycle regulatory events will perturb DNA replication fidelity, thereby contributing to neoplastic transformation. .
Figures



References
-
- Albanese C., Johnson J., Watanabe G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Johnson J., Watanabe G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Watanabe G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Arnold A., Pestell R.G., Pestell R.G. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Alt J.R., Cleveland J.L., Hannink M., Diehl J.A., Cleveland J.L., Hannink M., Diehl J.A., Hannink M., Diehl J.A., Diehl J.A. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cyclin D1 nuclear export and cyclin D1-dependent cellular transformation. Genes & Dev. 2000;14:3102–3114. - VSports注册入口 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bani-Hani K., Martin I.G., Hardie L.J., Mapstone N., Briggs J.A., Forman D., Wild C.P., Martin I.G., Hardie L.J., Mapstone N., Briggs J.A., Forman D., Wild C.P., Hardie L.J., Mapstone N., Briggs J.A., Forman D., Wild C.P., Mapstone N., Briggs J.A., Forman D., Wild C.P., Briggs J.A., Forman D., Wild C.P., Forman D., Wild C.P., Wild C.P. Prospective study of cyclin D1 overexpression in Barrett’s esophagus: Association with increased risk of adenocarcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000;92:1316–1321. - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
-
- Barnes D.M., Gillett C.E., Gillett C.E. Cyclin D1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1998;52:1–15. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
Publication types
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (VSports注册入口)
Research Materials (V体育安卓版)
Miscellaneous
