The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in CD4 T cells (V体育官网入口)
- PMID: 16542479
- PMCID: PMC1526596
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1905
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in CD4 T cells
"VSports app下载" Abstract
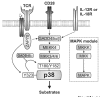
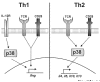
Since the identification of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) as a key signal-transducing molecule in the expression of the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF) more than 10 years ago, huge efforts have been made to develop inhibitors of p38 MAPK with the intent to modulate unwanted TNF activity in diseases such as autoimmune diseases or sepsis. However, despite some anti-inflammatory effects in animal models, no p38 MAPK inhibitor has yet demonstrated clinical efficacy in human autoimmune disorders. One possible reason for this paradox might relate to the fact that the p38 MAPK signaling cascade is involved in the functional regulation of several different cell types that all contribute to the complex pathogenesis of human autoimmune diseases. In particular, p38 MAPK has a multifaceted role in CD4 T cells that have been implicated in initiating and driving sustained inflammation in autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic vasculitis. Here we review recent advances in the understanding of the role of the p38 MAPK signaling cascade in CD4 T cells and the consequences that its inhibition provokes in T cell functions in vitro and in vivo VSports手机版. These new data suggest that p38 MAPK inhibitors may elicit several unwanted effects in human autoimmune diseases but may be useful for the treatment of allergic disorders. .
Figures
References (V体育官网)
-
- Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265:808–811. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
VSports注册入口 - Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
LinkOut - more resources (V体育平台登录)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"VSports在线直播" Research Materials

