"VSports注册入口" Effect of resveratrol and in combination with 5-FU on murine liver cancer
- PMID: 15378791
- PMCID: PMC4576270 (V体育ios版)
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.3048
Effect of resveratrol and in combination with 5-FU on murine liver cancer
Abstract
Aim: To study the anti-tumor effect of resveratrol and in combination with 5-FU on murine liver cancer VSports手机版. .
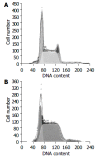
Methods: Transplantable murine hepatoma22 model was used to evaluate the anti-tumor activity of resveratrol (RES) alone or in combination with 5-FU in vivo. H22 cell cycles were analyzed with flow cytometry V体育安卓版. .
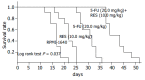
Results: Resveratrol could inhibit the growth of murine hepatoma22, after the mice bearing H22 tumor were treated with 10 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg resveratrol for ten days, and the inhibition rates were 36. 3% (n = 10) and 49. 3% (n = 9), respectively, which increased obviously compared with that in control group (85+/-22 vs 68+/-17, P<0 V体育ios版. 01). RES could induce the S phase arrest of H22 cells, and increase the percentage of cells in S phase from 59. 1% (n = 9) to 73. 5% (n = 9) in a dose-dependent manner (P<0. 05). The enhanced inhibition of tumor growth by 5-FU was also observed in hepatoma22 bearing mice when 5-FU was administered in combination with 10 mg/kg resveratrol. The inhibition rates for 20 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg 5-FU in combination with 10 mg/kg resveratrol were 77. 4% and 72. 4%, respectively, compared with the group of 20 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg 5-FU alone, in which the inhibition rates were 53. 4% and 43. 8%, respectively (n = 8). There was a statistical significance between the combination group and 5-FU group. .
Conclusion: RES could induce the S phase arrest of H22 cells and enhance the anti-tumor effect of 5-FU on murine hepatoma22 and antagonize its toxicity markedly VSports最新版本. These results suggest that resveratrol, as a biochemical modulator to enhance the therapeutic effects of 5-FU, may be potentially useful in cancer chemotherapy. .
Figures

References
-
- Kuang SY, Jackson PE, Wang JB, Lu PX, Muñoz A, Qian GS, Kensler TW, Groopman JD. Specific mutations of hepatitis B virus in plasma predict liver cancer development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:3575–3580. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Kew MC. Synergistic interaction between aflatoxin B1 and hepatitis B virus in hepatocarcinogenesis. Liver Int. 2003;23:405–409. - PubMed
-
- Chen HB, Huang Y, Dai DL, Zhang X, Huang ZW, Zhang QK, Wang HH, Zhang JS, Pan G. Therapeutic effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and percutaneous injection of acetic acids on primary liver cancer. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004;3:55–57. - PubMed
-
- Luo W, Birkett NJ, Ugnat AM, Mao Y. Cancer incidence patterns among Chinese immigrant populations in Alberta. J Immigr Health. 2004;6:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Chen JG, Parkin DM, Chen QG, Lu JH, Shen QJ, Zhang BC, Zhu YR. Screening for liver cancer: results of a randomised controlled trial in Qidong, China. J Med Screen. 2003;10:204–209. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources (V体育平台登录)
Full Text Sources (V体育2025版)
Medical

