Elucidating the Mechanism of Agrimonolide in Treating Colon Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology
- PMID: 37533972
- PMCID: PMC10390720
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S409530
Elucidating the Mechanism of Agrimonolide in Treating Colon Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology
Abstract
Purpose: This study reported the efficacy and underlying mechanism of agrimonolide (AM) in treating colon cancer. VSports手机版.
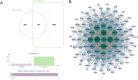
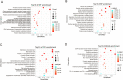
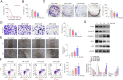
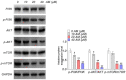
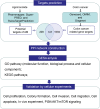
Methods: Colon cancer-AM-related targets were screened from online database. AM targets for colon cancer were identified by Venn diagram. Main molecular function, biological process, cellular component and pathways associated with AM targets for colon cancer were analyzed by GO and KEGG enrichment analysis. Relationship of the 10 core targets of AM for colon cancer with the top 15 BP and KEGG pathways was analyzed by Cytoscape software. A "component-target-pathway" network was constructed to select the hub genes of AM for colon cancer. AM effects on colon cancer cell viability, proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis were researched by CCK-8, colony formation, Transwell invasion, wound healing and flow cytometry assays. Tumor-bearing nude mice models were constructed and given AM treatment V体育安卓版. Hub gene expression in cells/tissues was detected by Western blot. .
Results: A total of 107 targets were selected as AM targets for colon cancer. The 10 core targets were related to the top 15 biological process terms and KEGG pathways. PI3K, AKT and mTOR were selected as the hub genes of AM for colon cancer. AM weakened colon cell proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis inhibition, and suppressed colon cell in vivo growth. AM up-regulated Caspase-3 and BAX proteins, down-regulated C-Myc, Cyclin D1 and BCL-2 proteins, and inactivated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway both in vitro and in vivo V体育ios版. .
Conclusion: AM suppressed colon cancer progression through inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. It may be useful for colon cancer treatment VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway; agrimonolide; colon cancer; in vivo; network pharmacology V体育平台登录. .
© 2023 Yu and Gai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures (V体育官网入口)



References
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

