C. spinosa L. subsp. rupestris Phytochemical Profile and Effect on Oxidative Stress in Normal and Cancer Cells
- PMID: 36235028
- PMCID: PMC9573631
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196488
"VSports最新版本" C. spinosa L. subsp. rupestris Phytochemical Profile and Effect on Oxidative Stress in Normal and Cancer Cells
Abstract
Spices, widely used to improve the sensory characteristics of food, contain several bioactive compounds as well, including polyphenols, carotenoids, and glucosynolates. Acting through multiple pathways, these bioactive molecules affect a wide variety of cellular processes involved in molecular mechanisms important in the onset and progress of human diseases. Capparis spinosa L. is an aromatic plant characteristic of the Mediterranean diet. Previous studies have reported that different parts (aerial parts, roots, and seeds) of C. spinosa exert various pharmacological activities. Flower buds of C. spinosa contain several bioactive compounds, including polyphenols and glucosinolates. Two different subspecies of C VSports手机版. spinosa L. , namely, C. spinosa L. subsp. spinosa, and C. spinosa L. subsp. rupestris, have been reported. Few studies have been carried out in C. spinosa L. subsp. rupestris. The aim of our study was to investigate the phytochemical profile of floral buds of the less investigated species C. spinosa subsp. rupestris. Moreover, we investigated the effect of the extract from buds of C. spinosa subsp. rupestris (CSE) on cell proliferation, intracellular ROS levels, and expression of the antioxidant and anti-apoptotic enzyme paraoxonase-2 (PON2) in normal and cancer cells. T24 cells and Caco-2 cells were selected as models of advanced-stage human bladder cancer and human colorectal adenocarcinoma, respectively. The immortalized human urothelial cell line (UROtsa) and human dermal fibroblast (HuDe) were chosen as normal cell models. Through an untargeted metabolomic approach based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF-MS), our results demonstrate that C. spinosa subsp. rupestris flower buds contain polyphenols and glucosinolates able to exert a higher cytotoxic effect and higher intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in cancer cells compared to normal cells. Moreover, upregulation of the expression of the enzyme PON2 was observed in cancer cells. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that normal and cancer cells are differentially sensitive to CSE, which has different effects on PON2 gene expression as well. The overexpression of PON2 in T24 cells treated with CSE could represent a mechanism by which tumor cells protect themselves from the apoptotic process induced by glucosinolates and polyphenols. .
Keywords: Capperis spinosa L. subsp. rupestris; cancer; glucosinolates; oxidative stress; paraoxonase; polyphenols V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement (V体育ios版)
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
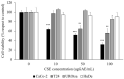
 ), human bladder carcinoma cells (T24) (
), human bladder carcinoma cells (T24) ( ), immortalized human urothelial cell line (UROtsa) (
), immortalized human urothelial cell line (UROtsa) ( ), and human dermal fibroblast (HuDE) (
), and human dermal fibroblast (HuDE) ( ). All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All reported values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *** Caco-2 vs. Caco-2 + CSE; ** T24 vs. T24+CSE; * UROtsa vs. UROtsa + CSE (ANOVA: *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.005; ***: p < 0.001).
). All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All reported values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *** Caco-2 vs. Caco-2 + CSE; ** T24 vs. T24+CSE; * UROtsa vs. UROtsa + CSE (ANOVA: *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.005; ***: p < 0.001).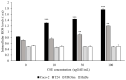
 ) and T24 (
) and T24 ( ) and normal cell lines UROtsa (
) and normal cell lines UROtsa ( ) and HuDE (
) and HuDE ( ). ROS levels were determined after 48 h of incubation. All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All reported values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation *** Caco-2 vs. Caco-2 + CSE; ** T24 vs. T24 + CSE(ANOVA: **: p < 0.005; ***: p < 0.001).
). ROS levels were determined after 48 h of incubation. All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All reported values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation *** Caco-2 vs. Caco-2 + CSE; ** T24 vs. T24 + CSE(ANOVA: **: p < 0.005; ***: p < 0.001).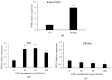
"VSports手机版" References
-
- Singh N., Yadav S.S. A review on health benefits of phenolics derived from dietary spices. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022;5:1508–1523. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.09.009. - V体育官网入口 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Medical

