V体育官网 - Application of Pickering emulsions in probiotic encapsulation- A review
- PMID: 36161224
- PMCID: PMC9493384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.09.013
"V体育2025版" Application of Pickering emulsions in probiotic encapsulation- A review
VSports最新版本 - Abstract
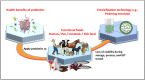
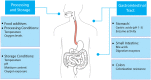
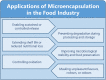
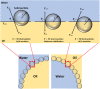
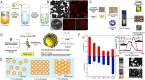
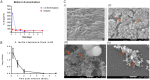
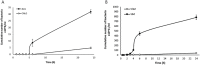
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits to host organisms when consumed in adequate amounts and are often incorporated into foods for human consumption. However, this has negative implications on their viability as large numbers of these beneficial bacteria are deactivated when subjected to harsh conditions during processing, storage, and passage through the gastrointestinal tract. To address these issues, numerous studies on encapsulation techniques to protect probiotics have been conducted. This review focuses on emulsion technology for probiotic encapsulation, with a special focus on Pickering emulsions. Pickering emulsions are stabilized by solid particles, which adsorb strongly onto the liquid-liquid interfaces to prevent aggregation VSports手机版. Pickering emulsions have demonstrated enhanced stability, high encapsulation efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to other encapsulation techniques. Additionally, Pickering emulsions are regarded as safe and biocompatible and utilize natural materials, such as cellulose and chitosan derived from plants, shellfish, and fungi, which may also be viewed as more acceptable in food systems than common synthetic and natural molecular surfactants. This article reviews the current status of Pickering emulsion use for probiotic delivery and explores the potential of this technique for application in other fields, such as livestock farming, pet food, and aquaculture. .
Keywords: Emulsions; Encapsulation; Pickering emulsions; Probiotics; Viability V体育安卓版. .
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Abdullah, Weiss J., Ahmad T., Zhang C., Zhang H. A review of recent progress on high internal-phase Pickering emulsions in food science. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;106:91–103. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.10.016. - VSports最新版本 - DOI
-
- Abesinghe A.M.N.L., Priyashantha H., Prasanna P.H.P., Kurukulasuriya M.S., Ranadheera C.S., Vidanarachchi J.K. Inclusion of probiotics into fermented buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) milk: an overview of challenges and opportunities. Fermentation. 2020;6(4):1–24. doi: 10.3390/fermentation6040121. - DOI
-
- Afzaal M., Khan A.U., Saeed F., Ahmed A., Ahmad M.H., Maan A.A., et al. Functional exploration of free and encapsulated probiotic bacteria in yogurt and simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019;7(12):3931–3940. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1254. - DOI (V体育平台登录) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anal A.K., Singh H. Recent advances in microencapsulation of probiotics for industrial applications and targeted delivery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007;18(5):240–251. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2007.01.004. - DOI
-
- Anjali T.G., Basavaraj M.G. Influence of pH and salt concentration on pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal peanuts. Langmuir. 2018;34(44):13312–13321. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02913. - V体育ios版 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

