The influence of PI3K inhibition on the radiotherapy response of head and neck cancer cells
- PMID: 33004905
- PMCID: PMC7529775
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73249-z
The influence of PI3K inhibition on the radiotherapy response of head and neck cancer cells
VSports在线直播 - Abstract
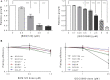
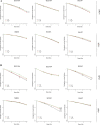
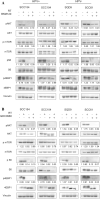
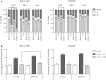
Radiotherapy has a central role in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway can decrease the efficiency of radiotherapy via the promotion of cell survival and DNA repair. Here, the influence of PI3K pathway inhibition on radiotherapy response was investigated. Two PI3K inhibitors were investigated and both BKM120 and GDC0980 effectively inhibited cellular and clonogenic growth in 6 HNSCC cells, both HPV-positive as well as HPV-negative. Despite targeted inhibition of the pathway and slight increase in DNA damage, PI3K inhibition did not show significant radiosensitization VSports手机版. Currently only one clinical trial is assessing the effectiveness of combining BKM120 with RT in HNSCC (NCT02113878) of which the results are eagerly awaited. .
"VSports app下载" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. - "V体育ios版" DOI - PubMed
-
- Hashibe M, et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007;99:777–789. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk179. - V体育ios版 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A, Sidransky D. Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;345:1890–1900. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra001375. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
Publication types (VSports在线直播)
"VSports注册入口" MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
Associated data
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育安卓版" Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

