Analysis of Expression and Its Clinical Significance of the Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32595698
- PMCID: PMC7303289
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00547
"VSports手机版" Analysis of Expression and Its Clinical Significance of the Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To explore the expression of secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and evaluate its relationship with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of LUAD, and analyze the advantages of SPP1 as a potential prognostic marker in LUAD VSports手机版. .
Methods: The expression of SPP1 in normal lung tissue and LUAD was analyzed from the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and Human Protein Atlas (HPA) databases V体育安卓版. GSE68465 was used to explore the relationship between the SPP1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics and the prognosis of LUAD patients. The relationship between SPP1 and immune infiltration in LUAD was analyzed by the Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) database. Gene enrichment analysis was performed in GSEA. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-LUAD data was used to verify the results. .
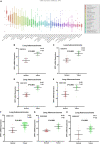
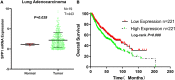
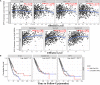
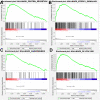
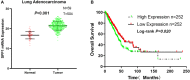
Results: In the cell line level, non-small cell lung cancer ranked ninth among cancer cell lines based on SPP1 expression. In the messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels, SPP1 expression was higher in LUAD tissues than that in normal control V体育ios版. SPP1 expression was related to gender, N stage, histological grade, and progression or relapse. In men, SPP1 expression were higher compared to that in women. The higher the N stage, the higher the SPP1 expression level. As LUAD progresses or relapses, SPP1 expression could increase. In the pathological grade, the SPP1 expression was higher in LUAD samples with moderate differentiation. In addition, the overall 5-year survival rates of the SPP1 high and low expression groups were 50. 574 and 59. 181% [P = 0. 008; hazard ratio (HR) = 0. 7057; 95% CI, 0. 5467-0. 9109], indicating that SPP1 had an impact on overall survival for LUAD patients. The relationship between SPP1 expression and CD4+ T cell, macrophage, neutrophil, and dendritic cell infiltration was weak in LUAD. SPP1 could be considered as an independent prognostic marker in LUAD (P = 0. 003; HR = 1. 150; 95% CI, 1. 048-1. 261) by multivariate Cox regression analysis. The results of GSEA indicated that samples with high SPP1 expression were enriched in protein secretion, mTORC1 signaling, angiogenesis, and glycolysis pathway. The analysis results obtained by TCGA-LUAD data were basically consistent with the results obtained by GSE68465. .
Conclusions: SPP1 can not only affect the occurrence and development of LUAD but also may be an independent prognostic marker of LUAD. SPP1 is expected to be a new target for molecular targeted therapy. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: bioinformatics; lung adenocarcinoma; osteopontin; prognosis; prognostic marker; secreted phosphoprotein 1. V体育平台登录.
Copyright © 2020 Guo, Huang, Wang, Liu, Li, Yao, Li and Hu VSports注册入口. .
Figures

References (V体育安卓版)
-
- Assidi M., Gomaa W., Jafri M., Hanbazazh M., Al-Ahwal M., Pushparaj P., et al. (2019). Prognostic value of Osteopontin (SPP1) in colorectal carcinoma requires a personalized molecular approach. Tumour. Biol. 41:1391226037. 10.1177/1010428319863627 - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Barretina J., Caponigro G., Stransky N., Venkatesan K., Margolin A. A., Kim S., et al. (2012). The cancer cell line encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 483 603–607. 10.1038/nature11003 - "VSports手机版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berardi R., Rinaldi S., Santoni M., Newsom-Davis T., Tiberi M., Morgese F., et al. (2016). Prognostic models to predict survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line chemo- or targeted therapy. Oncotarget 7 26916–26924. 10.18632/oncotarget.8309 - VSports在线直播 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee A., Richards W. G., Staunton J., Li C., Monti S., Vasa P., et al. (2001). Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 13790–13795. 10.1073/pnas.191502998 - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育2025版" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

