Loss-of-Function Variants in TBC1D32 Underlie Syndromic Hypopituitarism
- PMID: 32060556
- PMCID: V体育安卓版 - PMC7138537
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa078
VSports - Loss-of-Function Variants in TBC1D32 Underlie Syndromic Hypopituitarism
"V体育ios版" Abstract
Context: Congenital pituitary hormone deficiencies with syndromic phenotypes and/or familial occurrence suggest genetic hypopituitarism; however, in many such patients the underlying molecular basis of the disease remains unknown VSports手机版. .
Objective: To describe patients with syndromic hypopituitarism due to biallelic loss-of-function variants in TBC1D32, a gene implicated in Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) signaling. V体育安卓版.
Setting: Referral center V体育ios版. .
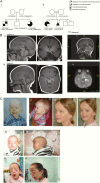
Patients: A Finnish family of 2 siblings with panhypopituitarism, absent anterior pituitary, and mild craniofacial dysmorphism, and a Pakistani family with a proband with growth hormone deficiency, anterior pituitary hypoplasia, and developmental delay. VSports最新版本.
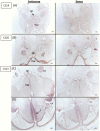
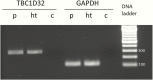
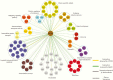
Interventions: The patients were investigated by whole genome sequencing. Expression profiling of TBC1D32 in human fetal brain was performed through in situ hybridization. Stable and dynamic protein-protein interaction partners of TBC1D32 were investigated in HEK cells followed by mass spectrometry analyses V体育平台登录. .
Main outcome measures: Genetic and phenotypic features of patients with biallelic loss-of-function mutations in TBC1D32 VSports注册入口. .
Results: The Finnish patients harboured compound heterozygous loss-of-function variants (c. 1165_1166dup p. (Gln390Phefs*32) and c. 2151del p. (Lys717Asnfs*29)) in TBC1D32; the Pakistani proband carried a known pathogenic homozygous TBC1D32 splice-site variant c. 1372 + 1G > A p. (Arg411_Gly458del), as did a fetus with a cleft lip and partial intestinal malrotation from a terminated pregnancy within the same pedigree V体育官网入口. TBC1D32 was expressed in the developing hypothalamus, Rathke's pouch, and areas of the hindbrain. TBC1D32 interacted with proteins implicated in cilium assembly, Shh signaling, and brain development. .
Conclusions: Biallelic TBC1D32 variants underlie syndromic hypopituitarism, and the underlying mechanism may be via disrupted Shh signaling VSports在线直播. .
Keywords: Sonic Hedgehog signaling; TBC1D32; ciliopathy; hypopituitarism; retinal dystrophy.
© Endocrine Society 2020.
VSports注册入口 - Figures
VSports在线直播 - References
-
- Bancalari RE, Gregory LC, McCabe MJ, Dattani MT. Pituitary gland development: An update. In: Mullis P-E, ed. Developmental Biology of GH Secretion, Growth and Treatment. Endocr Dev. Basel: Karger; 2012;23:1–15. - PubMed
-
- McCabe MJ, Dattani MT. Genetic aspects of hypothalamic and pituitary gland development. In: Handb Clin Neurol. Netherlands: Elsevier B.V; 2014;124:3–15. - PubMed
-
- de Moraes DC, Vaisman M, Conceição FL, Ortiga-Carvalho TM. Pituitary development: a complex, temporal regulated process dependent on specific transcriptional factors. J Endocrinol. 2012;215(2):239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports注册入口 - Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

