The interplay between HIF-1α and noncoding RNAs in cancer (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 32014012
- PMCID: PMC6998277 (VSports)
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-1535-y
The interplay between HIF-1α and noncoding RNAs in cancer
Erratum in
-
V体育平台登录 - Correction to: The interplay between HIF-1α and noncoding RNAs in cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 3;39(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01544-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32122375 Free PMC article.
Abstract
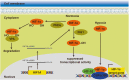
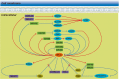
Hypoxia is a classic characteristic of the tumor microenvironment with a significant impact on cancer progression and therapeutic response. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α), the most important transcriptional regulator in the response to hypoxia, has been demonstrated to significantly modulate hypoxic gene expression and signaling transduction networks. In past few decades, growing numbers of studies have revealed the importance of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in hypoxic tumor regions. These hypoxia-responsive ncRNAs (HRNs) play pivotal roles in regulating hypoxic gene expression at the transcriptional, posttranscriptional, translational and posttranslational levels VSports手机版. In addition, as a significant gene expression regulator, ncRNAs exhibit promising roles in regulating HIF-1α expression at multiple levels. In this review, we briefly elucidate the reciprocal regulation between HIF-1α and ncRNAs, as well as their effect on cancer cell behaviors. We also try to summarize the complex feedback loop existing between these two components. Moreover, we evaluated the biomarker potential of HRNs for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer, as well as the potential clinical utility of shared regulatory mechanisms between HIF-1α and ncRNAs in cancer treatment, providing novel insights into tumorigenicity, which may lead to innovative clinical applications. .
Keywords: HIF-1α; carcinogenesis; clinical practice; ncRNA. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
"VSports最新版本" Figures
V体育官网入口 - References
-
- Lin SC, Liao WL, Lee JC, Tsai SJ. Hypoxia-regulated gene network in drug resistance and cancer progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2014;239(7):779–792. - PubMed
-
- Peitzsch C, Perrin R, Hill RP, Dubrovska A, Kurth I. Hypoxia as a biomarker for radioresistant cancer stem cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 2014;90(8):636–652. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell. 2010;40(2):294–309. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Shannon AM, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Condron CM, Toomey D. Tumour hypoxia, chemotherapeutic resistance and hypoxia-related therapies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2003;29(4):297–307. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Semenza GL. Intratumoral hypoxia, radiation resistance, and HIF-1. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(5):405–406. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports - Actions
"VSports在线直播" Grants and funding
"VSports注册入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

