Exosomal miRNAs in Lung Diseases: From Biologic Function to Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 31470655
- PMCID: PMC6781233
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8091345
Exosomal miRNAs in Lung Diseases: From Biologic Function to Therapeutic Targets
Abstract (VSports手机版)
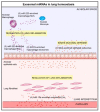
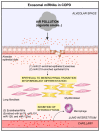
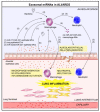
Increasing evidence suggests the potential role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in many lung diseases. According to their subcellular origin, secretion mechanism, and size, EVs are currently classified into three subpopulations: exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies. Exosomes are released in most biofluids, including airway fluids, and play a key role in intercellular communication via the delivery of their cargo (e. g. , microRNAs (miRNAs)) to target cell. In a physiological context, lung exosomes present protective effects against stress signals which allow them to participate in the maintenance of lung homeostasis. The presence of air pollution alters the composition of lung exosomes (dysregulation of exosomal miRNAs) and their homeostatic property VSports手机版. Indeed, besides their potential as diagnostic biomarkers for lung diseases, lung exosomes are functional units capable of dysregulating numerous pathophysiological processes (including inflammation or fibrosis), resulting in the promotion of lung disease progression. Here, we review recent studies on the known and potential role of lung exosomes/exosomal miRNAs, in the maintaining of lung homeostasis on one hand, and in promoting lung disease progression on the other. We will also discuss using exosomes as prognostic/diagnostic biomarkers as well as therapeutic tools for lung diseases. .
Keywords: acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome; asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; diagnostic biomarkers; exosomes; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung diseases; microRNAs; therapeutics V体育安卓版. .
"V体育安卓版" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- European Respiratory Society . Forum of International Respiratory Societies. European Respiratory Society; Sheffield, UK: 2017. The Global Impact of Respiratory Disease-Second Edition.
-
- WHO | Global Surveillance, Prevention and Control of Chronic Respiratory Diseases: A Comprehensive Approach. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012.
-
- Global Asthma Report 2014. [(accessed on July 10 2019)]; Available online: VSports最新版本 - http://www.globalasthmanetwork.org/news/GAR2014.php.
-
- Wardlaw T.M., Johansson E.W., Hodge M.J., UNICEF. Division of Communication. World Health Organization . Pneumonia: The Forgotten Killer of Children. World Health Organization and UNICEF; Geneva, Switzerland: 2006.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

