Circulating Tumour Cells (CTC), Head and Neck Cancer and Radiotherapy; Future Perspectives
- PMID: 30875950
- PMCID: PMC6468366
- DOI: "VSports在线直播" 10.3390/cancers11030367
Circulating Tumour Cells (CTC), Head and Neck Cancer and Radiotherapy; Future Perspectives
Abstract
Head and neck cancer is the seventh most common cancer in Australia and globally. Despite the current improved treatment modalities, there is still up to 50⁻60% local regional recurrence and or distant metastasis. High-resolution medical imaging technologies such as PET/CT and MRI do not currently detect the early spread of tumour cells, thus limiting the potential for effective minimal residual detection and early diagnosis. Circulating tumour cells (CTCs) are a rare subset of cells that escape from the primary tumour and enter into the bloodstream to form metastatic deposits or even re-establish themselves in the primary site of the cancer VSports手机版. These cells are more aggressive and accumulate gene alterations by somatic mutations that are the same or even greater than the primary tumour because of additional features acquired in the circulation. The potential application of CTC in clinical use is to acquire a liquid biopsy, by taking a reliable minimally invasive venous blood sample, for cell genotyping during radiotherapy treatment to monitor the decline in CTC detectability, and mutational changes in response to radiation resistance and radiation sensitivity. Currently, very little has been published on radiation therapy, CTC, and circulating cancer stem cells (CCSCs). The prognostic value of CTC in cancer management and personalised medicine for head and neck cancer radiotherapy patients requires a deeper understanding at the cellular level, along with other advanced technologies. With this goal, this review summarises the current research of head and neck cancer CTC, CCSC and the molecular targets for personalised radiotherapy response. .
Keywords: cf DNA; circulating cancer stem cells; circulating tumour cells; ctDNA; radiotherapy V体育安卓版. .
V体育官网 - Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing financial interests. V体育ios版.
Figures

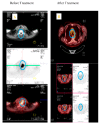

References (V体育平台登录)
-
- Dixit R., Weissfeld J.L., Wilson D.O., Balogh P., Sufka P., Siegfried J.M., Grandis J.R., Diergaarde B. Incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma among subjects at high risk of lung cancer: Results from the pittsburgh lung screening study. Cancer. 2015;121:1431–1435. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Head and Neck Cancer Statistics. [(accessed on 15 October 2017)]; Available online: https://head-neck-cancer.canceraustralia.gov.au/statistics.
-
- Ferlay J., Shin H.R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: Globocan 2008. Int. J. Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25516. - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports - Actions
LinkOut - more resources (V体育安卓版)
Full Text Sources

